Unlocking the Secrets of Microproteins: A Game Changer for Mitochondrial Health in Brown Fat
2025-09-01
Author: Nur
Mitochondria: The Powerhouses of Our Cells
Mitochondria are the unsung heroes of our cellular landscape, buzzing with energy and fueling our bodies similar to how bees nourish gardens. These tiny yet mighty organelles are crucial for maintaining life, yet their intricate workings depend on a cast of supporting molecules and proteins, many of which remain undiscovered.
A Breakthrough Study on Microproteins
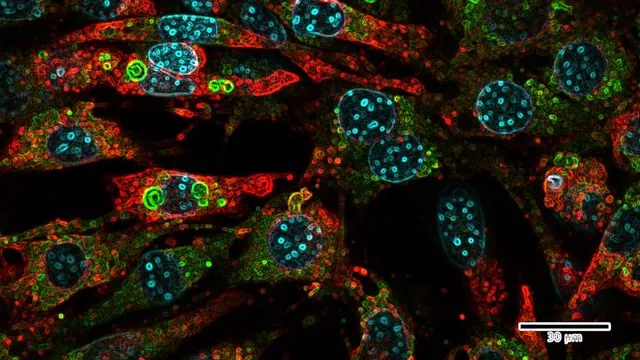
Researchers at the Salk Institute are diving deep into the world of microproteins—tiny proteins that have often been overlooked for their health and disease implications. Their latest study uncovers a newly identified microprotein, SLC35A4-MP, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining mitochondrial structure and managing metabolic stress within mouse fat cells. The implications of this research could pave the way for innovative treatments targeting obesity, aging, and various mitochondrial disorders.
Redefining the Role of Microproteins
Published on August 29, 2025, in *Science Advances*, this study is part of a wave of recent findings that emphasize the critical roles microproteins play in cellular biology and stress responses. Senior author Alan Saghatelian notes that these microproteins, previously dismissed as mere genetic debris, are actually vital regulators of cell function. He highlights that the newly discovered microprotein is essential for the integrity of mitochondrial function in brown fat tissue, which is responsible for regulating body temperature and energy balance.
A Revolutionary Finding in Genetics
The journey to discover SLC35A4-MP began in late spring 2024, when Saghatelian’s team found its genetic code hidden within an upstream open reading frame on messenger RNA (mRNA). This discovery challenged the conventional wisdom that each mRNA corresponds to one protein, revealing that these upstream segments could code for functional microproteins instead.
Demonstrating Physiological Significance in Living Systems
Though earlier research suggested microproteins like SLC35A4-MP contributed to healthy cellular metabolism in lab settings, the ultimate test of their function required studying them in live organisms. According to first author Andréa Rocha, the team successfully demonstrated that SLC35A4-MP is vital for regulating mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism in living mice, underscoring the importance of these proteins in biological health.
A Closer Look at Brown Fat Cells
To better understand the significance of SLC35A4-MP, the researchers examined brown fat cells, which are highly metabolically demanding. They completely removed SLC35A4-MP from these cells and then subjected the mice to stressful conditions such as cold exposure and high-fat diets. The results were alarming: without SLC35A4-MP, the mice struggled to ramp up their metabolism in cold conditions, exhibiting structurally compromised mitochondria that were inflamed and dysfunctional.
Broader Implications for Health and Disease
The findings reveal SLC35A4-MP’s fundamental role in bolstering brown fat cell function and resilience to metabolic stress. Given that mitochondria are present in nearly every cell type, the implications of this research stretch far and wide—potentially offering new therapeutic avenues for tackling diseases that disrupt metabolic and mitochondrial function, from obesity to age-related conditions.
The Bright Future of Microprotein Research
As research on microproteins continues to blossom, the Salk team is optimistic about discovering more of these functional proteins. Saghatelian emphasizes the increasing awareness of microproteins as important physiological regulators, which could inject new life into scientific inquiry focused on cellular health.
The journey to fully understand microproteins is just beginning, and their potential to transform our approach to health and disease is nothing short of exhilarating.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)