Shocking Links: Pregnancy Adversities and Birth Defects Uncovered!
2025-09-01
Author: Yu
Investigating the Hidden Dangers of Pregnancy
A groundbreaking study reveals that adverse events during pregnancy significantly elevate the risk of congenital malformations in newborns. Despite existing research, the full extent of these dangers and their underlying mechanisms remain largely unexplored, raising urgent questions about maternal health.
Methodology: A Revolutionary Approach to Understanding Risks
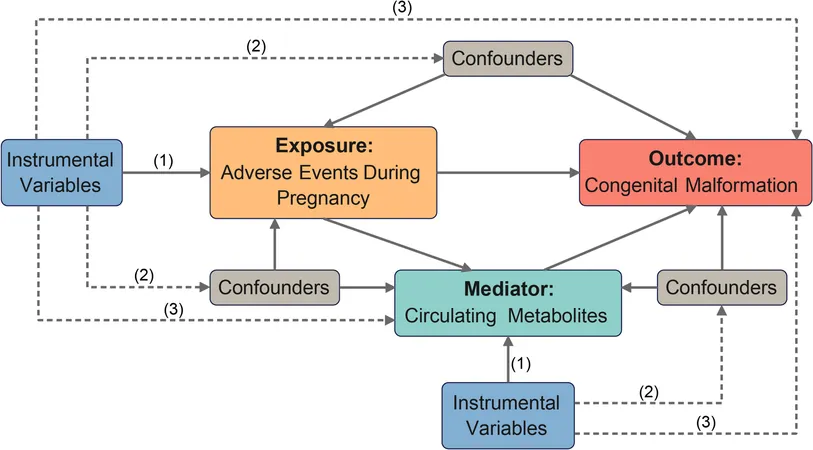
In a pioneering effort, researchers conducted a Mendelian randomization study. This innovative two-sample and two-step approach assesses the link between adverse pregnancy events and congenital conditions while examining how circulating metabolites play a mediating role. By analyzing genetic data, the study aims to untangle the complexities of these relationships.
Key Findings: What Every Expecting Mother Should Know
#### Maternal Bleeding: A Double-Edged Sword Maternal bleeding during pregnancy appears to heighten the risk of congenital ichthyosis (a skin disorder) while surprisingly reducing the likelihood of congenital hydrocephalus (water on the brain). #### Anemia's Dire Consequences Anemia has been found to correlate significantly with atrioventricular septal defects, a serious heart condition in infants. #### The Risks of Placental Issues Placental issues, such as placenta previa and placental abruption, immediately raise concerns—they are tied to an increased risk of breast malformations yet may reduce hydrocephalus.
Premature Birth and Heart Defects: A Life-Threatening Connection
Premature birth is also notable, linking directly to higher risks for complex heart defects. Meanwhile, fetal malposition surprisingly correlates with a lower risk of cleft lip, adding complexity to the threat landscape.
Infection Mid-Pregnancy: A Heart Wrenching Reality
Urogenital infections during pregnancy were linked to alarming rates of cardiac malformations, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring and immediate treatment of infections.
Unlocking the Mystery: Glycine's Role
Interestingly, glycine, a common amino acid, is posited to mediate a small percentage of the relationship between premature birth and heart defects—about 1.1%. This highlights how critical nutrition is in fetal development and the potential impact of maternal health.
A Call for More Research
Despite these intriguing results, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive and require further investigation through clinical trials and additional studies to fully comprehend these findings.
Harnessing Genetic Insights to Mitigate Risks
Using genetic variations, this groundbreaking study seeks to understand the impact of pregnancy adversities on congenital disorders. While ensuring methodological rigor, the research adheres to strict guidelines, thus fortifying its findings.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap in Maternal and Fetal Health Research
This study fills crucial gaps in understanding the link between adverse pregnancy events and birth defects, advocating for holistic care approaches to maternal health. As researchers continue to peel back the layers, this critical evidence calls for deeper exploration and awareness, ultimately safeguarding the future of countless newborns.
A Hopeful Future: Better Understanding Means Better Outcomes
As these revelations make their way into clinical practices, expectant mothers may soon benefit from enhanced strategies aimed at staving off potential complications. Continuous research in this realm is essential as pregnant women navigate their journey towards motherhood.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)