The Rising Tide of Depression: An Alarming Surge in Major Depression Among Young People Worldwide
2025-04-18
Author: Jia
A Global Mental Health Emergency
Over the last few decades, major depression disorder (MDD) has evolved into a pressing global health crisis, particularly among adolescents and young adults aged 10 to 24. Data reveals a startling increase in diagnosed cases, jumping from approximately 45 million in 1990 to 70 million by 2021. The trend is not just a statistic—it's a reflection of the changing mental health landscape shaped by various socioeconomic factors.
Understanding the Stats: The Impact of MDD
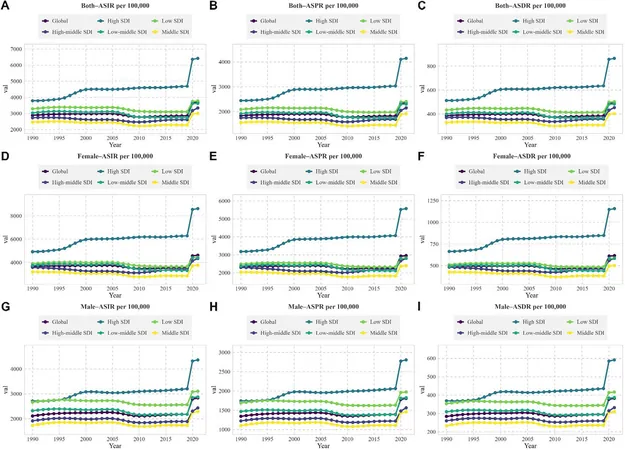
Incredibly, global figures indicate that 42 million females and 27 million males were living with major depression as of 2021. The age-standardized incidence rates (ASIR) and prevalence rates (ASPR) illustrate the increasing severity of the situation. For young people, this disorder is more than just numbers; it translates to real-life consequences, including significant years lost to disabilities.
The Role of Socioeconomic and Regional Disparities
Interestingly, the effect of socioeconomic factors is profound. Regions categorized by higher Socio-Demographic Indices (SDI) demonstrated dramatic increases in MDD rates. High- and high-middle SDI regions saw their ASIR and ASPR rates double post-2020, underscoring how wealthier areas are also grappling with mental health challenges. In contrast, middle- and low-SDI regions, despite experiencing less pronounced increases, still faced substantial burdens.
Youth at Risk: Trends Over Time
Data analysis from 1990 to 2021 indicates a continual rise in MDD incidence, pinpointing the 20-24 age group as particularly vulnerable. Adolescents (age 10-19) also exhibited increasing rates, revealing that youth—especially females—are navigating an unprecedented mental health crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated these issues, leading to heightened anxiety and depression among teenagers.
Breaking Down the Causes: Risk Factors at Play
Several risk factors contribute to the growing burden of MDD—bullying victimization, intimate partner violence, and childhood sexual abuse are leading culprits. Bullying alone accounted for a staggering percentage of mental health-related disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in many regions, notably Central Sub-Saharan Africa.
Looking Ahead: Projecting Future Trends
From 2021 to 2045, projections suggest that the global burden of MDD will continue to rise, impacting both males and females. Targeted interventions are essential in schools and communities to combat this growing epidemic. The data also highlights the urgent need for mental health resources tailored to address gender-specific and age-related needs.
The Call to Action for Global Mental Health
As MDD encroaches upon the wellbeing of younger generations, it's clear that urgent action is needed. Policymakers must prioritize mental health through school programs, public awareness campaigns, and community resources. Addressing the disparate impact of MDD across various socioeconomic landscapes is critical to reducing its long-term effects. We stand at a pivotal point; the stakes have never been higher for our youth.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)