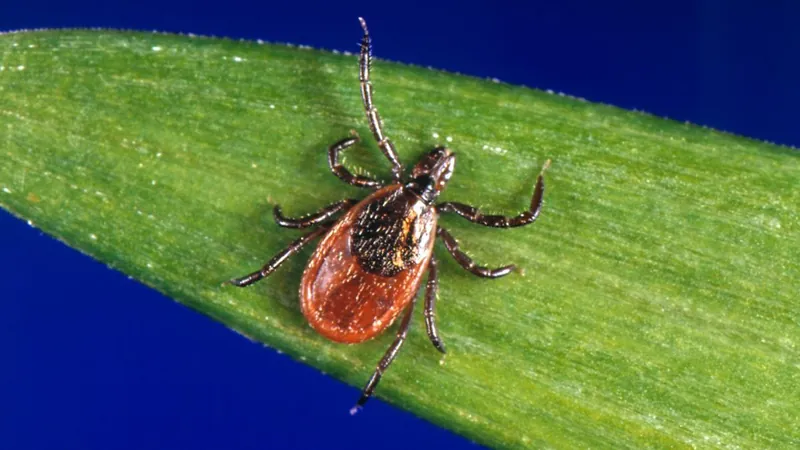

What You Need to Know About Babesiosis: The Parasitic Menace That Destroys Your Red Blood Cells!
2025-03-20
Author: Sarah
Understanding Babesiosis: A Global Threat
Babesiosis is a rare yet potentially deadly parasitic infection characterized by the destruction of red blood cells—those vital cells that transport oxygen from our lungs to every part of the body. Transmitted primarily through tick bites, this condition is found around the globe, making it a serious concern not just in the U.S., but also in various regions across Europe and beyond.
In the United States alone, fewer than 3,000 cases of babesiosis are reported each year, most frequently during the warmer months between May and September. The disease is most prevalent in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions, including states like Minnesota, Wisconsin, Connecticut, and New York, where the population comes into more frequent contact with ticks.
The Unseen Invaders: How Babesia Parasites Attack
Babesiosis is caused by microscopic parasites belonging to the genus Babesia. These parasites primarily affect the red blood cells of their hosts. While over 100 species of Babesia exist, only a handful are known to infect humans. The most common species in the U.S. is Babesia microti, which is primarily spread by blacklegged ticks, also known as deer ticks.
Interestingly, the transmission of Babesia can also occur through blood transfusions or from mother to fetus during pregnancy, highlighting its versatility and potential for spread beyond just tick bites.
Who’s at Risk? Know Your Vulnerabilities
Not everyone exposed to Babesia parasites will show symptoms; healthy young individuals often remain asymptomatic. However, the risk increases significantly for older adults, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those who have had their spleen removed. These groups are particularly susceptible to severe forms of the disease.
Symptoms of babesiosis usually manifest within one to four weeks of exposure and may include fever, chills, sweating, muscle aches, an enlarged liver and spleen, and a dangerously low red blood cell count. Serious cases can escalate to multiorgan failure and death, especially if oxygen deprivation reaches critical levels.
A Grim Reality: The Death Toll Linked to Babesiosis
While estimates of mortality rates from babesiosis vary, the CDC reported a 0.57% death rate among infected individuals in the U.S. This figure climbs dramatically among high-risk groups—where death rates can reach 20% despite medical intervention.
Getting Treated: What Options Are Available?
Generally, those without symptoms do not require treatment as their immune systems can clear the infection naturally within a couple of weeks. For symptomatic patients, treatment typically involves a regimen of antiparasitic medications combined with antibiotics, which can be surprisingly effective even though they primarily target bacterial infections.
In cases of severe infection, where red blood cells are critically compromised, blood transfusions may be necessary to restore oxygen-carrying capacity in the body.
Preventive Measures: Protect Yourself!
Given the risks associated with babesiosis, especially in tick-infested areas, adopting preventive measures is crucial. Wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities can help reduce the likelihood of infection.
In summary, babesiosis may be rare but it poses significant risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. Stay informed, stay protected, and don’t take any chances with your health!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)