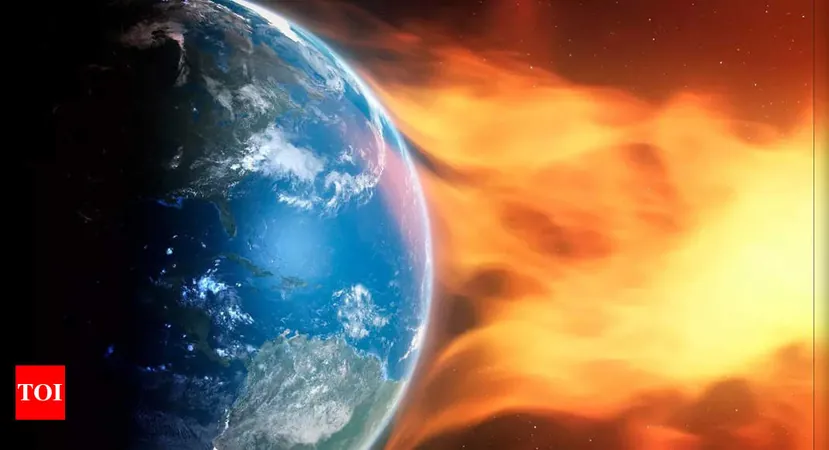

Unraveling the Mysteries of Geomagnetic Storms: What You Need to Know!
2024-11-03
Author: Mei
On October 28th, residents across the northern United States were treated to an enchanting spectacle as the Northern Lights illuminated the skies, a stunning display triggered by intense solar flare activity. States like Idaho, South Dakota, and New York witnessed the vibrant aurora borealis, captivating sky gazers and astronomy enthusiasts alike.
This breathtaking phenomenon was not spontaneous; it stemmed from a series of powerful solar flares emitted by the Sun. Specifically, on October 28th, an X-class solar flare erupted from two sunspot regions identified as 3872 and 3873. X-class flares are classified as the most potent type of solar flare, capable of significantly impacting the Earth's magnetosphere, leading to geomagnetic storms that can disrupt communication systems and power grids on Earth.
What Exactly is a Geomagnetic Storm?
A geomagnetic storm occurs when there is a disturbance in the Earth's magnetosphere, primarily caused by solar wind and magnetic fields released during solar activity. These storms are graded on a five-level scale by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC). On that fateful Monday, the geomagnetic activity was rated at a level 2 (out of 5), indicating that the Northern Lights could be viewed much farther south than is usually possible, thus expanding the audience for this extraordinary light show.
Warnings and Preparations
With the heightened solar activity detected, NOAA issued a Geomagnetic Storm Watch on the preceding Sunday, as satellites recorded coronal mass ejections (CMEs) heading towards Earth. These CMEs represent massive bursts of solar wind and magnetic fields, which can lead to increased geomagnetic storm activity. By Monday morning, the watch was escalated to a Geomagnetic Storm Warning, confirming the potential for significant auroral displays and warning communities to be prepared for possible disruptions in technology and communication systems.
Where to View the Aurora Borealis?
On the night of October 28, 2024, some of the most spectacular displays of the Northern Lights could be seen across the northern tier of the United States. Residents in Idaho, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Wisconsin were particularly fortunate, as were observers on the East Coast in northern New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, and parts of Maine. The awe-inspiring sight attracted not only locals but also tourists and photographers who aimed to capture this fleeting natural wonder.
Why Should You Care?
Geomagnetic storms don't just create visual spectacles; they can have real impacts on modern technology. High levels of solar activity can disrupt satellite operations and GPS signals, and can even affect electrical grids, leading to power outages. Understanding these storms can help us better prepare for such events in the future.
So, as solar activity continues to evolve, keep an eye on alerts from NOAA. You never know when the stunning aurora borealis might grace your skies again—leaving you in awe of our universe’s sheer magnificence!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)