Unlocking the Secrets of Wnt Signaling: A New Protein Superfamily Emerges
2025-09-09
Author: Nur
Groundbreaking Discovery in Protein Evolution
In a stunning revelation, researchers have identified a vast and previously overlooked family of enzymes, dubbed the Lipocone superfamily. This discovery traces their evolutionary journey from bacterial defense molecules to vital components in human development, shining a light on their significance across various biological kingdoms.
Published in the renowned journal eLife, this study is heralded as a pivotal exploration into the lineage, structure, and function of these essential molecules, many of which have not received previous attention.
Meet Wnt: The Key Player in Development and Disease
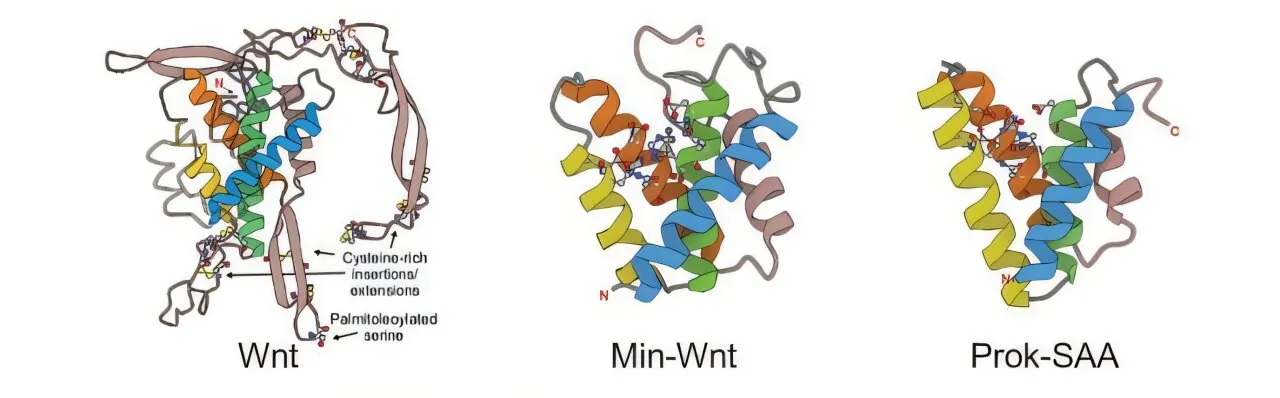
Central to this superfamily is Wnt, a protein known for its crucial roles in the development of animals and humans. It's also linked to several diseases, including many types of cancer. Despite being discovered four decades ago, the evolutionary roots of Wnt remained largely enigmatic until recent findings.
Co-lead researcher A. Maxwell Burroughs from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) shares, "In 2020, we unveiled the first bacterial variants of Wnt, highlighting their characteristics as toxins in biological conflict, much like how they fend off viruses. This spurred us to delve deeper into their evolutionary links and potential functions."
Dismantling Evolutionary Mystery: The Lipocone Superfamily
The team's exploration revealed that bacterial and metazoan (multicellular) Wnt share a unique ancestral design with a distinctive alpha-helical core. They conducted comprehensive sequence searches, identifying a common structural motif across 30 diverse protein families, of which 17 were previously uncharacterized.
Upon examining these families, the researchers noted variations in hydrophobicity, suggesting that many members could naturally align with lipid-rich cellular membranes. This connection influenced the name of the newly defined Lipocone superfamily.
AI-Powered Insights: Predicting Structure and Function
Utilizing AlphaFold, an advanced AI tool, the team predicted the three-dimensional structure of superfamily members from their amino acid sequences. Their exploration indicated that these proteins might share a common biochemical function: modifying lipid head groups and managing critical cell structures.
A Saga of Evolution: From Bacteria to Proteins
In a quest for evolutionary clarity, the authors reconstructed the diversification timeline of the Lipocone superfamily. They identified an ancestral protein, ultimately leading to 30 distinct families tied to vital roles in lipid metabolism, antibiotic resistance, inter-bacterial conflict, and immune responses.
Wnt: From Enzyme to Cell Communicator
One remarkable finding highlights Wnt's transformation from an active enzyme to an inactive state, maintaining its role in cell signaling. Co-lead author Gianlucca Nicastro notes, "Wnt might not function as an enzyme anymore, but it still possesses a distinctive binding pocket, hinting at potential interactions with other molecules, including lipids."
Significance of the Lipocone Superfamily in Biochemistry
In summary, the senior author L. Aravind emphasizes that this discovery opens up fresh paths in understanding lipid biochemistry and illuminates the origins of Wnt signaling. It also raises new questions about immunity and the complex interactions that occur across the Tree of Life, setting the stage for future research in protein evolution.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)