Unlocking the Secrets of Brown Algae: A Leap Forward in Biotechnology
2025-04-10
Author: Wei
Revolutionary Discoveries from the Depths of the Sea
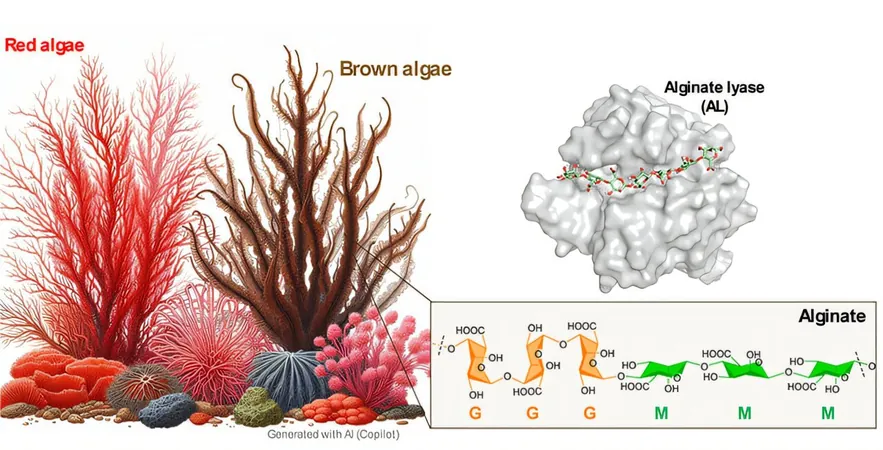
Brown algae, a treasure trove of natural compounds, are being harvested in massive quantities each year, yielding valuable substances like alginates—sugars that boast remarkable strength and density. But what happens behind the scenes? A groundbreaking study led by the University of Barcelona has finally uncovered the secret mechanism of an enzyme called alginate lyase (AL), revealing how it breaks down these marine materials for innovative uses.
Transforming Nature’s Bounty into Biotech Gold
Published in the prestigious journal *Nature Communications*, this research paves the way for harnessing 'tailored alginates'—customized forms of these compounds suitable for various applications, particularly in food and biomedical sectors. This development could revolutionize how these natural resources are exploited in biotechnology.
Meet the Scientific Heroes Behind the Breakthrough
The international team, spearheaded by José Pablo Rivas-Fernández and Carme Rovira from the University of Barcelona, collaborated with experts from prestigious institutions, including Denmark’s Technical University and the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Together, they tackled the complexities of alginates, which are often plagued by a varied composition of sugars, creating challenges in their biotechnological potential.
Cracking the Enzyme Code for Better Biotech Solutions
The real magic lies in understanding how AL enzymes interact with and deconstruct the alginate polymer. This insight addresses the limitations of natural alginates, which vary in their sugar compositions—specifically, mannuronic and guluronic acids. As the team elaborated, this knowledge lays the foundation for optimizing enzyme manipulation, aiming for enhanced catalytic efficacy on an industrial scale.
A Greener Future: Boosting the Green Economy
The implications of this study stretch beyond simple scientific curiosity. By refining the way we use enzymes to produce alginates, this research heralds a new era of sustainability in biotech, promoting better resource utilization and fostering a robust green economy.
Unveiling the Mechanisms with Cutting-Edge Technology
To delve deeper, the researchers utilized the cutting-edge MareNostrum 5 supercomputer to conduct complex simulations. These simulations revealed critical insights, such as the nature of the reaction that occurs in a single stage, rather than multiple phases, which could reshape current understandings of enzyme behavior.
The Future Looks Bright for Biotechnological Applications
By identifying key amino acid residues within the enzyme that drive its efficiency, the research opens new avenues for genetic engineering, enabling scientists to design better variants of alginate lyase. Moreover, it enhances our understanding of alginate’s chemical evolution during degradation—a crucial factor in isolating and utilizing alginate lyases yet to be discovered. UB researchers are poised to create innovative probes to identify these enzymes, setting the stage for future advancements.
Conclusion: A New Dawn for Biotech Innovations
This remarkable research not only sheds light on the fundamental workings of enzymes involved in alginate degradation but also holds promise for the next generation of biotechnological breakthroughs. As we unlock the secrets of brown algae, the potential for novel applications continues to grow, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient future.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)