Unlocking the Secrets of Antimony: A Game Changer for Phase Change Materials!
2025-01-22
Author: Daniel
A New Era in Materials Research
A recent groundbreaking study sheds new light on the chemical bonding characteristics of antimony, potentially revolutionizing materials research. This collaborative effort by scientists from Leipzig University, RWTH Aachen University, and the renowned DESY synchrotron in Hamburg merges experimental investigations with theoretical framework, promising transformative advances in technology.
Significant Contributions to Phase Change Materials
The research, published in the prestigious journal Advanced Materials, makes significant contributions to our grasp of phase change materials. These materials are crucial for innovations in data storage systems and thermoelectrics, which convert temperature differences into electrical energy.
Understanding Bond Strengths
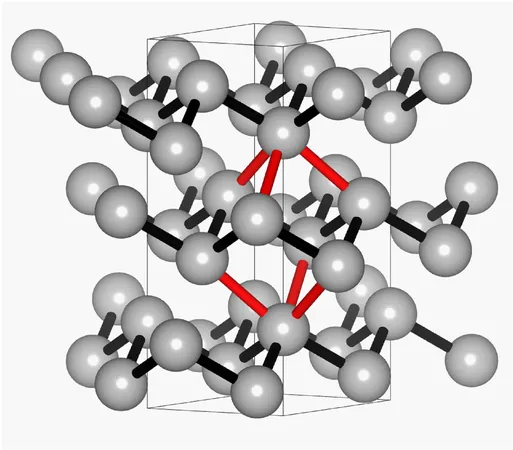
Professor Claudia S. Schnohr from Leipzig University's Felix Bloch Institute for Solid State Physics emphasizes the importance of understanding bond strengths: "The strength of a bond depends directly on the distance between the atoms. Our comparisons with metals and semiconductors reveal that this distance dependence is a defining characteristic of the type of chemical bond."
Covalent Bonding vs. Multi-Center Bonding
One of the most intriguing revelations of the study is the discovery of a seamless transition between classical covalent bonding and electron-rich multi-center bonding. Covalent bonds are commonly observed in semiconductors like germanium, and researchers found that antimony in its stable phase exhibits traits of both bonding types. Co-author Professor Oliver Oeckler from the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry and Crystallography notes, "This bodes well for the application of antimony in modern technology."
Antimony as a Model for Phase Change Materials
The team specifically focused on antimony as a model for phase change materials due to its unique structural properties that mirror those of germanium telluride while consisting of just one type of atom. This simplicity allows for a clearer analysis, paving the way for enhanced understanding and innovation in the field.
The Future of Data Storage and Energy Conversion
As the demand for faster, more efficient data storage and energy conversion technologies increases, this research could catalyze significant advancements. With the potential to improve the functionality and efficiency of phase change materials, antimony’s unique bonding characteristics may hold the key to unlocking a new era of technological development.
Conclusion
Stay tuned, as the implications of this research could change the landscape of materials science and technology dramatically!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)