
Unlocking Earth's Secrets: Biomass Satellite Captivates with Stunning First Images
2025-06-24
Author: Sarah
A New Era in Earth Observation Begins
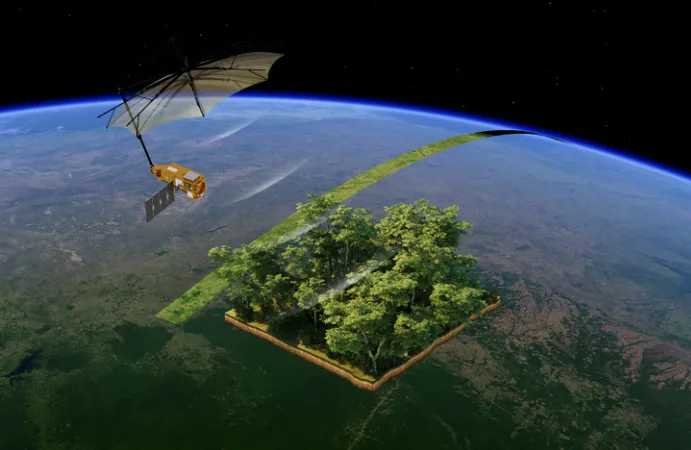
The recently launched Biomass satellite, part of ESA’s FutureEO program, is making waves with its inaugural images that promise to revolutionize our understanding of the planet's ecosystems. Beyond simply capturing stunning views of forests, this pioneering mission hints at greater insights into Earth’s extreme environments.
Cutting-Edge Technology at Work
Launched less than two months ago, the Biomass satellite is currently in its commissioning phase, where its technology is being fine-tuned to deliver precise data. Michael Fehringer, ESA's Biomass Project Manager, expressed enthusiasm, stating, "These first images are spectacular and a mere glimpse of what’s to come. We're ensuring the satellite operates at peak performance to accurately gauge global carbon storage in our forests."
Unmatched Insights into Carbon Storage
Equipped with a groundbreaking P-band synthetic aperture radar, Biomass penetrates forest canopies to assess woody biomass, such as trunks and branches, which correlate with carbon storage. While the initial data is still being calibrated and can't yet quantify carbon, early results indicate Biomass is on the right path to achieving its ambitious objectives.
Essence of Forests and Ecosystems
ESA’s Director of Earth Observation Programmes, Simonetta Cheli, noted that these first images illustrate the satellite’s potential to drastically enhance our comprehension of Earth's forests. By integrating advanced radar technology with expertise, the mission aims to yield essential insights regarding carbon dynamics and our planet's forest health.
A Closer Look at Deforestation in Bolivia
Among the most striking images taken is a detailed view of Bolivia—a nation grappling with substantial deforestation rates due to agricultural expansion. The colorful radar representation reveals distinct land features, with green shades indicating rainforests, red highlighting forested floodplains, and areas marked in blue and purple showing grasslands. Water bodies such as rivers and lakes are depicted in black.
The Wonders of the Amazon Basin
One remarkable feature captured is the Beni River, which winds from the Andes through Bolivia and into Brazil. This dynamic river truly embodies the historical and ecological narrative of the Amazon, which is still untamed by manmade barriers.
Mapping the Future of Forests
The true strength of the Biomass mission lies not only in capturing a snapshot of the landscape but in its ability to profile multiple observations of the same area over time. This technique allows scientists to accurately assess forest height and carbon reserves, deepening our understanding of tropical forests and their role in the global carbon cycle.
Exploring Hidden Structures Beneath the Surface
The potential applications of Biomass extend beyond forests; its radar can penetrate up to five meters into dry sand, uncovering geological features like ancient riverbeds in arid regions. Such insights could enhance our understanding of past climates and the search for fossil water resources.
Illuminating Climate Change Dynamics
Moreover, the radar's capability to penetrate ice layers offers crucial data on ice movement and internal ice structure, providing insights that shorter-wavelength radars cannot achieve. This opens new avenues for understanding climate change and its impacts on polar regions.
A Journey Just Beginning
As the Biomass satellite continues its mission, we can anticipate a treasure trove of information that could transform our approaches to environmental management and conservation. This mission not only symbolizes a technological leap but also reaffirms our commitment to safeguarding the planet for future generations.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)