Transforming Environmental Monitoring: Breakthrough in Remote Sensing Time Series Analysis
2024-12-22
Author: Ming
Introduction
As urban areas expand and environmental conditions fluctuate, the demand for precise and timely terrestrial monitoring has become more critical than ever. A groundbreaking review introduces a cutting-edge method in remote sensing time series analysis that merges data from multiple sources, allowing for near real-time monitoring of environmental changes. This advancement is set to revolutionize environmental conservation and urban planning by delivering unparalleled insights into the dynamics of our planet.
Scientific Collaboration and Challenges Addressed
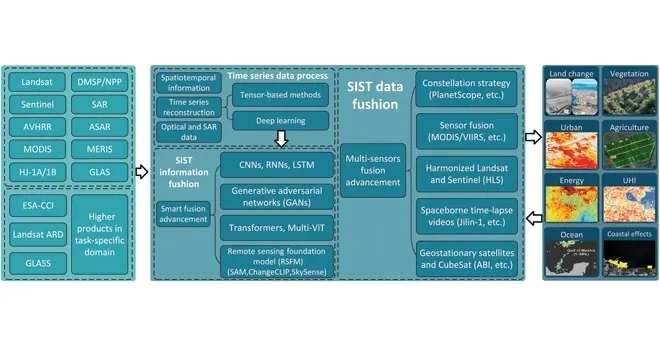
In a notable scientific collaboration, researchers from South China Normal University, the University of Connecticut, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have made significant strides in remote sensing technology. Their review, recently published in the Journal of Remote Sensing, addresses prevalent challenges such as incomplete datasets and noise interference that have historically plagued remote sensing efforts. The new time series analysis technique employs advanced data reconstruction and fusion methods, marking a leap forward in the accuracy and effectiveness of monitoring environmental changes.
Innovative Techniques in Data Analysis
The innovative technique utilizes deep learning algorithms alongside traditional remote sensing methods to effectively aggregate data from various platforms. This hybrid approach is vital for extracting nuanced patterns within extensive and complex datasets, essential for tracking critical environmental indicators like land usage and vegetation health. Unlike earlier methodologies that often falter in the face of incomplete or erratic data, this new model enhances reliability and offers more insightful analyses of earth's dynamics.
LSTM Networks and GANs
A key to the study's success lies in incorporating Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). LSTM networks excel at capturing evolving trends over time, while GANs generate synthetic data to fill in gaps caused by missing or distorted observations. This dual methodology has led to the creation of a cleaner and more accurate time series dataset, validated against independent measurements on the ground. The research demonstrated remarkable enhancements in key vegetation indices, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), establishing a new standard in the remote sensing domain.
Potential Impact and Future Applications
Experts are excited about the potential of this technology to transform the landscape of remote sensing applications. They regard the method as a groundbreaking tool for high-resolution environmental monitoring, promising vast improvements in agricultural oversight, urban development, and environmental management. As Professor Fu aptly put it, “This method represents a crucial advancement in our ability to monitor environmental changes. With further development, it could become integral in combating climate change and other global challenges.”
Conclusion
In summary, the cutting-edge advancements in remote sensing time series analysis herald a new era for environmental monitoring that could significantly influence policy and practice globally. Keep an eye on this transformative technology—it may well become crucial in our collective efforts to sustain the planet for future generations!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)