The Hidden Dangers of Hantavirus: Insights from a 20-Year Study in South Korea
2025-08-22
Author: Siti
Hantavirus Rising: A Urgent Call for Action
The alarming spread of zoonotic diseases tied to Orthohantaviruses, particularly Hantavirus hantanense (HTNV), has become a critical public health concern. These viruses, primarily associated with rodents, lead to Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS), and South Korea sees between 400 to 500 reported cases annually. This trend highlights an urgent need for thorough risk assessments and preventive measures.
Rodent Reservoirs: The Main Culprits
HTNV is predominantly linked to the striped field mouse, Apodemus agrarius, which is integral to the majority of HFRS cases in South Korea. Other strains, like O. seoulense (SEOV) found in rats, contribute to about 20% of cases but with much lower fatality rates. The study indicates that human exposure mainly occurs through inhalation of aerosolized materials from infected rodents, underscoring the need for vigilance in rural and military areas, especially those with rodent infestations.
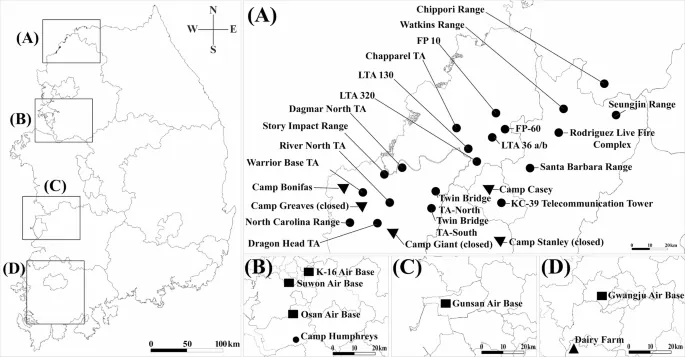
Longitudinal Insights: A 20-Year Snapshot
Examining data collected over two decades, researchers captured a staggering 12,476 small mammals, predominantly A. agrarius. The study reveals that the highest capture rates were near military training sites, emphasizing the critical link between rodent population dynamics and HFRS outbreaks.
Seasonal Trends: A Perfect Storm for Infection
HFRS incidence shows clear seasonal peaks, with the fall marking the most significant surge in cases, coinciding with the maturation of naive juvenile rodents. Increased human activities, especially in agriculture and military training during these times, further exacerbate the risk of hantavirus transmission.
Mapping Out Risk: Assessing Hantavirus Hotspots
The researchers devised a comprehensive risk assessment model pinpointing high-risk areas, primarily in northern Gyeonggi and Gangwon Provinces. Factors such as the density of seropositive rodents and environmental conditions that promote dust generation were critical in identifying these hotspots.
The Future: Strategies for Prevention
With insights from this extensive research, there’s a pressing need for integrated strategies aimed at reducing human infection risks. These include habitat modifications, enhancing rodent surveillance, and educating military personnel about preventative measures. The study suggests a multi-pronged approach balancing immediate health concerns with long-term ecological sustainability to combat the threat of HFRS.
Understanding Rodent Behavior: The Key to Prevention
To better understand how HFRS outbreaks can be managed, further investigations into rodent behavior and ecological factors affecting transmission dynamics are essential. With the right mix of research and practical applications, we can pave the way for safer environments, especially in high-risk areas.
Conclusion: The Battle Against Hantavirus Continues
This pivotal research sheds light on the intricate relationship between rodent populations and zoonotic diseases, revealing the crucial steps needed to mitigate HFRS risks in South Korea. As we delve deeper into this hidden danger, the commitment to effective surveillance and ecological awareness remains paramount in our ongoing battle against hantavirus.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)