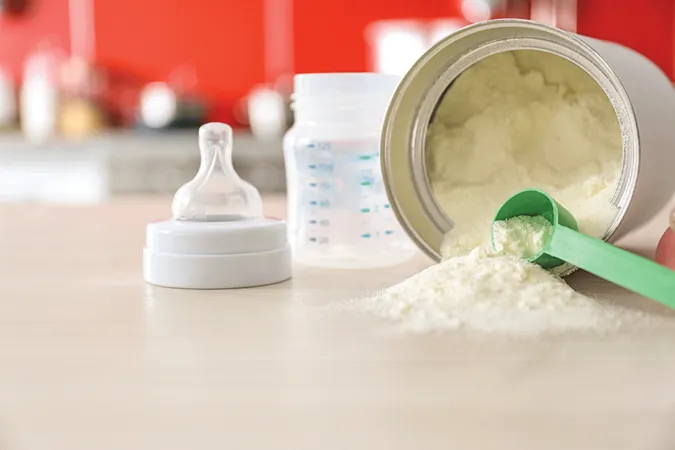

The DGAC Calls for Clarity on Ultra-Processed Foods: What You Need to Know!
2024-12-26
Author: Sarah
Introduction
In a groundbreaking development, the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) for 2025 has raised a crucial alarm regarding ultra-processed foods, stating that a clear definition must be established before any dietary recommendations can be confidently made. This revelation was highlighted in their recent scientific report, which reflects upon the importance of adapting dietary guidelines to fit various cultures and income levels.
Current Dietary Recommendations
The DGAC reaffirmed existing guidelines from the 2020-2025 Dietary Recommendations, maintaining that total saturated fat and sugar intake should each constitute less than 10% of total caloric consumption. This consistency underlines the ongoing concern related to how these dietary components influence overall health.
Health Impacts of Ultra-Processed Foods
Diving deeper into the health impacts of ultra-processed foods, the committee analyzed how consumption ties into issues such as growth, body composition, and obesity. Strikingly, they noted limited evidence linking a higher intake of these foods with increased fat mass and a greater likelihood of obesity. However, this analysis is hampered by the absence of a standardized definition of what constitutes an ultra-processed food, which the DGAC clearly stated as a major obstacle.
Expert Insights
Joanne Slavin, PhD, a member of the advisory committee and a renowned professor at the University of Minnesota, emphasized that some products like infant formula could fall into this category. She cautioned against the potentially dangerous idea of creating homemade infant formula, underscoring the importance of regulated products for vulnerable populations.
Future Research Directions
The DGAC emphasized the need for future committees to rigorously examine ultra-processed foods in relation to obesity and body composition. Currently, the committee's findings suggest that these foods often contain higher levels of saturated fats, sodium, and added sugars, alongside various preservatives and additives, which could pose health risks if consumed excessively.
Health Equity Considerations
Another significant focus of the report was health equity. The DGAC highlighted that dietary choices are influenced by a variety of factors including psychological, sociological, and economic conditions, all of which are intertwined with cultural backgrounds. As the U.S. population grows increasingly diverse, the committee pointed out the necessity for dietary guidelines to be culturally relevant and accessible, particularly for minority communities and those with lower income levels. Slavin proposed that dietary information be made available in discount grocery stores to help reach these populations effectively.
Recommendations for Public Health
In addressing concerns about saturated fat, Slavin recommended opting for plant-based sources rich in healthy fats and fiber. Additionally, reducing sugar intake, particularly from beverages, was cited as an essential step toward improving public health.
Conclusion
Though the DGAC has made recommendations, Slavin noted that the definitive 2025-2030 Dietary Guidelines for Americans will ultimately be shaped by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Stay tuned for more updates as the dialogue around ultra-processed foods continues to evolve—will you continue to consume them without a clear definition of what they are?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)