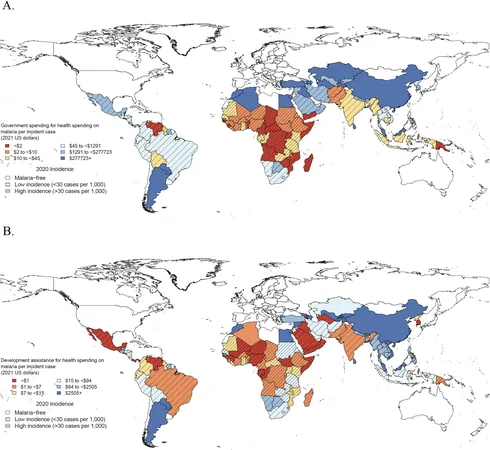
The Battle Against Malaria: How Efficient Spending Could Save Thousands of Lives
2024-11-09
Author: Daniel
Malaria continues to be a deadly foe, claiming an estimated **750,000 lives** in 2021 alone, with a staggering **700,000** of those occurring in sub-Saharan Africa. Alarmingly, nearly **60%** of these victims were children under five years old. However, a silver lining emerges as malaria-related mortality has notably decreased by **35%** globally from 1990 to 2021, primarily attributed to advancements in treatment and prevention strategies, alongside substantial global financial commitments. The establishment of international health organizations such as the **Global Fund** and the **President’s Malaria Initiative** has bolstered this endeavor.
Despite these strides, progress has stalled over the last decade, with a meager growth of **3.5%** per year in development assistance for malaria between 2011 and 2019, compared to a robust **28.9%** from 2000 to 2010. Similarly, government investments have cooled to **4.3%** annual growth through 2017. This stagnation emphasizes the urgent need for malaria-endemic countries to dissect their spending strategies — prioritizing effective funding can lead to significant improvements in tackling malaria.
Recent research is sparse regarding which types of malaria spending yield the most significant health outcomes. Notable studies have attempted to analyze funding efficiency, showcasing models that could avert significant deaths and cases if resources are better allocated, such as focusing on **long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs)** and seasonal malaria chemoprevention. A groundbreaking study by the **Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME)** aimed to fill this gap, estimating comprehensive malaria spending across endemic countries from 2000 to 2020, breaking down funds into **eleven key program areas**.
These program areas include essential components like **anti-malarial medications**, **diagnostics**, and **procurement management**. By drawing on a rich reservoir of data and employing advanced statistical modeling techniques, they uncovered the correlations between types of spending and health outcomes — paving the way towards understanding how countries can optimize their malaria spending for maximum impact.
Key Findings:
1. **Varied Spending Efficiency**: The research revealed stark distinctions in spending efficiency based on the disease burden. Low-burden countries spent more per incident case; this misallocation in funding is detrimental, especially when combating a resurgent disease.
2. **Focus on Prevention Pays Off**: Countries investing in preventive strategies such as **ITNs** showed promising results, proving that targeting high-risk areas leads to better outcomes. The analysis indicated that a larger allocation of funding toward development assistance and prevention strategies correlated with higher efficiency in reducing incidence rates.
3. **Emerging Exemplar Countries**: Argentina, Paraguay, and Turkmenistan showcased remarkable efficiency in managing incidence rates alongside their expenditure. Their success stories demonstrate that a combination of political commitment, strategic funding allocation, and community engagement have yielded tangible results.
4. **Long-term Investments Reap Rewards**: Continuous investment in malaria control measures reflects on a nation's efficiency. For instance, countries like Sri Lanka have seen remarkable drops in case fatality rates, suggesting a robust health system supported by effective financing strategies for anti-malarial medications and quality healthcare access.
The Road Ahead
Significantly, the importance of leveraging comprehensive malaria control strategies cannot be overstated. These findings highlight an urgent need for improved international cooperation and funding directed towards the most effective interventions that can truly save lives. As countries strategize to eliminate malaria, focusing on data-driven approaches will be crucial in ensuring that every dollar spent translates to real-world health improvements.
Conclusion
As the world grapples with multiple health challenges, the fight against malaria remains a paramount concern. Efficient spending on anti-malarial strategies is key to turning the tide in this ongoing battle. The time is ripe for governments and donors to reassess their priorities and ensure their investments yield the maximum possible impact in saving lives, especially among the most vulnerable populations. The landscape of malaria management can and must change—your support, even if it’s just spreading awareness, can make a difference!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)