
Stunning Fossil Discovery in Brazil Could Revolutionize Our Understanding of Dinosaur Evolution
2024-11-14
Author: Siti
Stunning Fossil Discovery in Brazil Could Revolutionize Our Understanding of Dinosaur Evolution
In the serene landscapes of southern Brazil, specifically in the little-known region of Paraíso do Sul, a remarkable fossil has been unearthed—one that could change everything we know about the evolution of dinosaurs. This exceptional find belongs to a newly identified reptile species dubbed Gondwanax paraisensis, which thrived approximately 237 million years ago during the Triassic period, a pivotal era marked by explosive evolutionary experimentation on Earth.
This dog-sized creature, measuring about 39 inches long and featuring a long tail, is classified as a member of an extinct group known as silesaurids. While not true dinosaurs, these reptiles are closely related and are vital to understanding the origins of the iconic giants that would later dominate the Mesozoic era.
Rodrigo Temp Müller, the paleontologist leading this groundbreaking study at the Federal University of Santa Maria in Brazil, emphasized the significance of the fossil's age: "Because it's so old, it gives us clues as to how dinosaurs came to be." This statement underlines the potential of Gondwanax paraisensis to shed light on the evolutionary pathway of dinosaurs, challenging and perhaps even rewriting existing theories.
The ongoing scientific discourse surrounding silesaurids positions them either as ancestors of true dinosaurs or as a sister group that diverged from a common lineage. Some researchers propose that certain silesaurids might have evolved directly into ornithischians—herbivorous dinosaurs with bird-like pelvic structures, such as the armored Stegosaurus and the massive Triceratops. Understanding this connection could illuminate the physical traits that heralded the success of the earliest dinosaurs.
However, reconstructing this evolutionary narrative is fraught with challenges due to the fragmentary state of many silesaurid fossils. This has left scientists grappling with differing interpretations of their evolutionary significance.
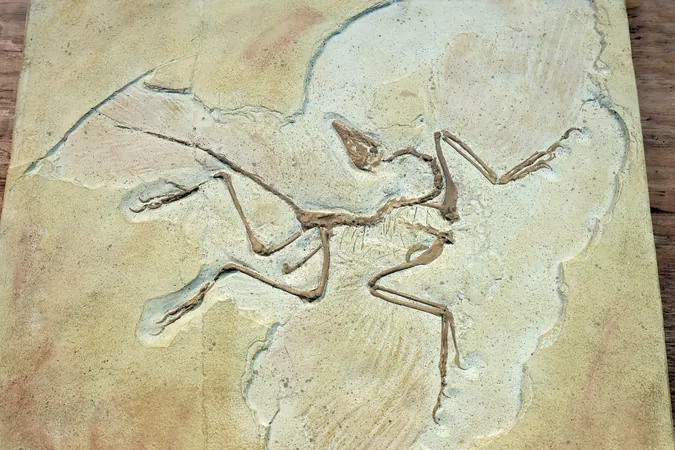
The excitement surrounding this find was deeply felt by physician Pedro Lucas Porcela Aurélio, who stumbled upon the fossil in 2014. "Being the first human to touch something from 237 million years ago is extraordinary," he commented, sharing the awe of connecting with a distant past. From its rocky encasement, visible only were the vertebrae, which revealed surprising insights. Unlike its relatives that typically had two vertebrae in their hips, Gondwanax featured three—a trait that hints at its more dinosaur-like characteristics.
If further analysis validates this hypothesis, it could extend our understanding of ornithischians' origins by a staggering ten million years and reshape our perspective on how these early creatures came to be.
Yet as thrilling as this discovery is, paleontologists like Steve Brusatte of the University of Edinburgh caution that more fossil evidence is essential to solidify these findings. "I wish I could say that this new silesaurid fossil solves the riddle once and for all," Brusatte acknowledged, indicating that the quest for understanding continues.
In the midst of continued research and the pursuit of additional fossil evidence, the mystery surrounding this dog-sized reptile persists. Its discovery serves as a poignant reminder of the ancient life that once roamed our planet and underscores the ever-evolving narrative of dinosaur evolution. With every fossil uncovered, we inch closer to illuminating the secrets of our prehistoric past, offering tantalizing glimpses into the lives of creatures that walked the Earth millions of years ago.
Stay tuned as this thrilling scientific story unfolds, and prepare to rethink everything you thought you knew about dinosaurs!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)