Surge in Respiratory Infections Among Children in Central China: Groundbreaking Study Reveals Alarming Trends
2025-08-22
Author: Arjun
A Closer Look at Respiratory Infections in Henan Province
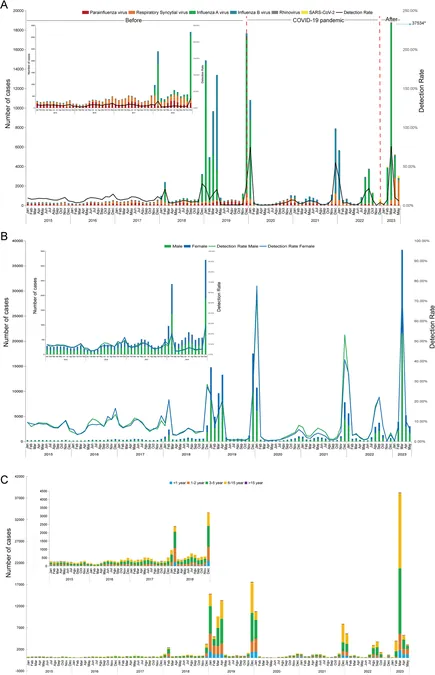
From 2015 to 2023, a staggering 183,771 cases of respiratory viral infections emerged in Henan Province, China. The most common culprits? Influenza A (Flu A) dominated the scene with a mind-blowing 58.66% detection rate, followed by other pathogens like Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Influenza B, and SARS-CoV-2.
Unraveling Co-Infection Patterns
Among the infected, 3,976 patients (a notable 2.16%) suffered from co-infections. The predominant combination? Flu A paired with Flu B, found in 1,221 cases. In 2023 alone, co-infection rates surged, with alarming peaks in triple infections occurring in 2021.
Fluctuating Serotypes Over the Years
Between 2015 and 2017, Parainfluenza Virus (PIV) and RSV held sway. However, from 2018 onward, a shift occurred as Flu A took the lead, especially during 2021 when Flu B outshone the others. The implications? Different viral strains emerged as leaders in severe cases across the years, with a notable rise in SARS-CoV-2 influence post-2020.
Understanding Age Vulnerability
The data reveals sobering realities for the youngest. Kids under 1 year faced critical illness rates of 29.28%. This highlights a jaw-dropping vulnerability due to their still-developing immune systems, especially in comparison to older age groups.
Seasonal Trends of Respiratory Infections
The study uncovered seasonal peaks for various viruses, generally around winter and spring. But Flu A showed an unusual spike in March, challenging the expected trends. Such irregularities have profound implications for future vaccination campaigns.
Post-COVID Trends in Symptoms and Severity
The clinical landscape is changing. Pre-COVID, persistent symptoms such as cough and fever were common, but after the pandemic, severe cases skyrocketed, especially with pneumonia and respiratory failure. The rise of new symptoms post-2023 emphasizes the ongoing evolution of respiratory threats.
Exploring Gender Disparities in Infections
Interestingly, a gender gap exists, with males exhibiting a significantly higher infection rate (57.22%) than females. This intriguing finding warrants further investigation into potential behavioral and biological factors contributing to this disparity.
The Implications of Co-Infection Risks
The intricate interplay of co-infections raises major concerns about increased hospitalization and mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable groups. The prevalent combo of Flu A and Flu B illustrates the threat of concurrent viral circulation.
Navigate the Future: Public Health Recommendations
As we move forward in a post-pandemic world, understanding these shifts is essential for crafting targeted public health strategies. Prioritize education on infection prevention in schools and childcare settings, ramp up immunization efforts, and enhance surveillance systems for early detection.
Conclusion: Get Ready for the Next Wave
This comprehensive study shines a spotlight on the evolving landscape of respiratory viral infections among children in Henan. With insights drawn from the recent past and alarming trends emerging, the need for robust public health planning and adaptive strategies is paramount. As we navigate these complexities, vigilance will be key in safeguarding our children from respiratory threats.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)