
Shockingly New Black Hole Discoveries by Hubble Telescope Could Rewrite Cosmic History!
2024-09-26
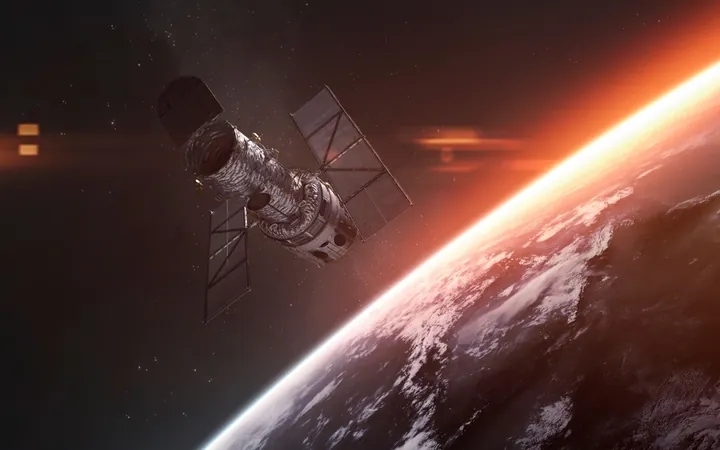
In a remarkable turn of events, the Hubble Space Telescope has discovered an unexpected abundance of black holes in the early universe, significantly altering our understanding of cosmic history. These astonishing revelations indicate that black holes formed in galaxies less than a billion years after the Big Bang are not only more numerous but also more massive than previously thought.
Unearthing the Mysteries of Early Black Holes
Recent observations made by Hubble reveal that there are far more early black holes than astronomers had counted before. This new data suggests that these black holes emerged during an era when the universe was still in its infancy, less than a billion years old. Scientists believe that many of them formed from the dramatic collapse of large, pristine stars—in essence, the universe's first heavyweights.
Connecting Black Holes and Galaxies
Black holes play pivotal roles in the cosmic drama of galaxy evolution. They are not just bystanders but rather active contributors to the lifecycle of galaxies. Through its advanced observational technologies, Hubble is allowing scientists to explore the complex relationships between these enigmatic black holes and their galactic hosts.
Understanding how black holes grow in tandem with galaxies can refine existing models of galaxy formation. Insights gathered from Hubble’s findings can uncover how galaxies, including our Milky Way, evolved into their present structures and behaviors.
Origins of Black Holes in the Universe
The formation of black holes has long been a field of intense scientific inquiry, particularly during the formative years of the universe. Here are some primary methods by which these mysterious entities can originate:
1. **Collapsing Massive Stars:** Massive stars exhaust their nuclear fuel and collapse, creating black holes. 2. **Primordial Black Holes:** Hypothetical black holes theorized to form just moments after the Big Bang. 3. **Collapsing Gas Clouds:** Gigantic clouds of gas can gather enough gravitational force to collapse and form black holes. 4. **Galactic Mergers:** When galaxies collide, they can produce giant black holes from the remnants of stars.
Each of these methods contributes to our understanding of how black holes affect their host galaxies and play a crucial role in cosmic evolution.
The Unsurpassed Legacy of the Hubble Space Telescope
For more than 30 years, the Hubble Space Telescope has stood as a beacon of astronomical research, consistently delivering groundbreaking discoveries that have reshaped our comprehension of the universe. Its detailed observations not only identify celestial phenomena but also provide invaluable insights into the intricate workings of black holes, many of which were previously shrouded in mystery.
Managed by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), the Hubble telescope has proven to be an indispensable instrument for scientists seeking to understand the cosmos. The telescope's ongoing mission continues to refine our understanding of black hole origins, formations, and their consequential relationships with galaxies.
Implications for Cosmic Understanding
The incredible findings regarding early black holes offer a fresh perspective that may challenge existing theories surrounding the formation of supermassive black holes. These newly observed black holes display greater mass than scientists had previously anticipated, prompting a re-evaluation of our understanding of how these cosmic giants come into existence.
By drawing from Hubble's precise observations, researchers can advance their models of galaxy development and aim to paint a clearer picture of our universe's evolution. The implications of this groundbreaking discovery are staggering—who knows what other secrets still lie hidden in the cosmos, waiting to be uncovered?



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)