
Shocking Links Revealed: Maternal Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severely Increases Pregnancy Risks!
2024-11-06
Author: Arjun
Groundbreaking Study Findings
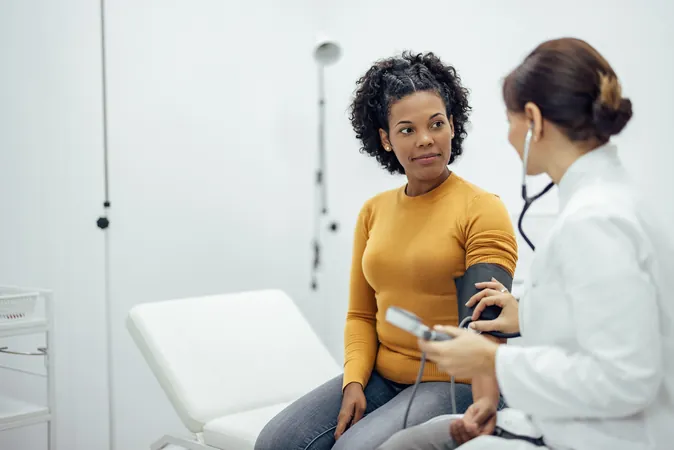
A groundbreaking study has found a troubling association between maternal hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and heightened risks for both pregnancy complications and adverse outcomes for mothers and their newborns. The research, which analyzed data from over 1 million births in Quebec, Canada, indicates that expectant mothers suffering from HS face an alarming array of health challenges.
Understanding Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder marked by the presence of painful, swollen lesions. This condition is not just a source of physical distress; it can also lead to a range of psychosocial issues due to associated pain and scarring, especially since HS predominantly affects women aged 21 to 29.
Study Overview
In this extensive longitudinal cohort study spanning from April 2006 to March 2022, researchers collected maternal and neonatal health data to assess outcomes. The study included women diagnosed with HS who required hospitalization around the time of their pregnancy and evaluated them against a control group of mothers without HS.
Key Findings
A staggering 1,324,488 deliveries were reviewed, revealing that just 1,332 (0.1%) of these mothers had HS. Notably, those with HS were found to be significantly younger and included a higher percentage of women who experienced various pre-existing health conditions and socioeconomic disadvantages.
Health Risks for Mothers
The results were striking: mothers with HS had a 55% increased risk of hypertensive disorders during pregnancy and a 61% increased risk for gestational diabetes. Additionally, these women faced a greater likelihood of severe conditions, including postpartum hemorrhage and even the need for intensive care pre- and post-delivery.
Risks for Newborns
The consequences weren’t limited to the mothers; neonates born to mothers with HS were 28% more likely to be born prematurely and exhibited a 29% increased risk for birth defects, particularly concerning congenital heart defects and orofacial clefts.
Long-Term Implications
Even more alarming, long-term follow-up showed that mothers with HS were 2.29 times more likely to face hospitalization for various reasons later in life compared to their peers, while their children had a 31% higher risk of hospitalization due to respiratory, metabolic, psychiatric, and immune-related issues.
Call for Further Research
However, the researchers emphasized that while these findings are significant, several limitations may affect their generalizability. Potential misclassification of HS cases and the observational nature of the study mean further investigations are necessary to ascertain causal relationships.
Implications for Healthcare
The study draws critical attention to this highly prevalent condition among women of childbearing age, urging healthcare professionals to closely monitor pregnant patients diagnosed with HS and to consider long-term follow-ups for infants born to these mothers.
Future Directions
Given these significant risks, the findings have stirred conversations in medical communities about better screening and intervention strategies for expecting mothers with hidradenitis suppurativa. The call for vigilance in managing these patients has never been more urgent!
Conclusion
This eye-opening research highlights an essential area of women's health that has long been overlooked. Could this discovery change the fate of countless mothers and their children? Stay tuned for more developments!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)