Shocking Discovery: China's Zhurong Rover Unveils Evidence of an Ancient Ocean on Mars!
2024-11-08
Author: Jia
Shocking Discovery: China's Zhurong Rover Unveils Evidence of an Ancient Ocean on Mars!
In a groundbreaking revelation, data from China's Mars rover Zhurong has brought to light compelling evidence suggesting that Mars may have once harbored a vast ancient ocean, offering new insights into the Red Planet's geological past and its potential to sustain life!
A study published in the esteemed journal Scientific Reports highlights a remarkable collaboration between in situ data collected by the Zhurong rover and remote sensing observations. These findings showcase features indicative of an ancient nearshore environment flourishing in the northern lowlands of Mars.
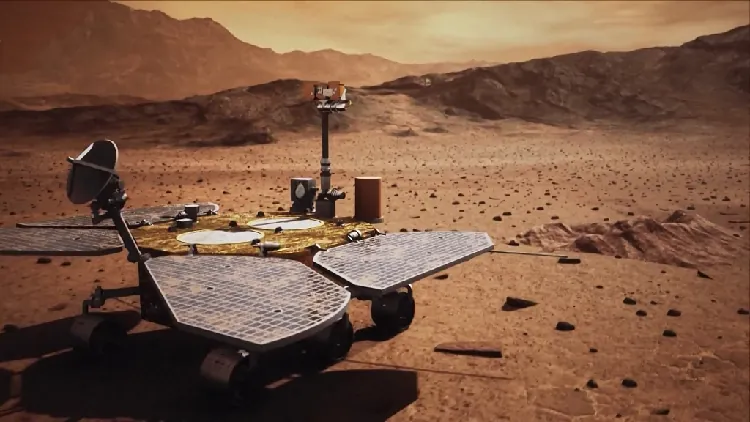
The Zhurong rover, a star element of China's revolutionary Tianwen-1 mission, gracefully touched down on Utopia Planitia, a sprawling plain located in Mars’ northern hemisphere, back in 2021. This mission was explicitly designed to explore the geology of Mars, and the latest analyses imply that a significant flooding event transpired on Utopia Planitia approximately 3.68 billion years ago. According to Bo Wu, a planetary scientist at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, "The ocean surface was likely frozen for a geologically brief period."
This remarkable study uncovers a variety of marine landscape features in southern Utopia. Researchers identified distinct areas, including a foreshore highland-lowland transition, a shallow marine zone, and deeper marine environments—these observations suggest a complex evolution indicative of the northern lowlands undergoing significant transformations during the Late Noachian epoch.
Experts estimate that this once-thriving ocean vanished around 3.42 billion years ago, as Mars transitioned to the frigid, arid landscape we see today. Co-author Sergey Krasilnikov noted, "The water was heavily silted, leading to the layering structure of the deposits found."
While prior studies hinted at the existence of a Hesperian ocean in Mars’ northern lowlands, this fresh data refines our understanding of its extent and characteristics. The research proposes that the region experienced several distinct stages: an initial flooding, alongside the creation of shallow and deep marine areas during the Early Hesperian epoch, culminating in the eventual loss of subsurface volatiles in the Amazonian epoch.
These water-related geological features could revolutionize our understanding of Mars’ habitability. "The idea of an ancient ocean on Mars has been speculated for decades, yet much uncertainty persists," Wu emphasized.
Crucially, these findings not only bolster the theory of a Martian ocean but also ignite discussions about its potential evolutionary scenario for the very first time. This existence of water significantly raises the tantalizing possibility that Mars once supported microbial life, a key element necessary for life as we know it!
Interestingly, during the period when this ocean thrived, Mars may have been in the processes of losing its once dense atmosphere, shifting from a climate more akin to Earth. "In Mars' early history, when it likely had a warm, thick atmosphere, the potential for microbial life would have been heightened," Krasilnikov added.
As scientists continue to investigate these astonishing discoveries, the prospect of ancient marine environments on Mars not only expands our understanding of our neighboring planet but also fuels the dream of unraveling the mysteries of extraterrestrial life. Stay tuned for more updates as this story unfolds!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)