Revolutionizing Stroke Recovery: The Promise of High-Frequency Magnetic-Stimulation for Enhanced Motor Function
2024-09-19
Overview
In the quest to combat the debilitating aftermath of strokes, groundbreaking research is heralding hope for patients grappling with motor dysfunction. A recent study protocol introduces high-frequency magnetic paired associative stimulation, a novel therapeutic approach aimed at restoring motor function in ischemic stroke patients, where traditional methods have often fallen short.
Background
Stroke has emerged as one of the leading causes of long-term disability globally, and with the aging population, its prevalence continues to rise. In China, staggering statistics reveal that over 80% of stroke victims suffer from contralateral upper limb hemiplegia, with more than 40% left with lingering motor deficits, including muscle weakness and impaired coordination. These impairments significantly hinder simple daily activities, underscoring the urgent need for innovative rehabilitation techniques.
The neurological damage inflicted by strokes disrupts essential sensorimotor integration networks, which are crucial for coordinating voluntary movements. Recent studies have shown that a significant proportion of acute stroke patients struggle with basic tasks due to impaired hand and arm positioning, emphasizing the need for effective interventions.
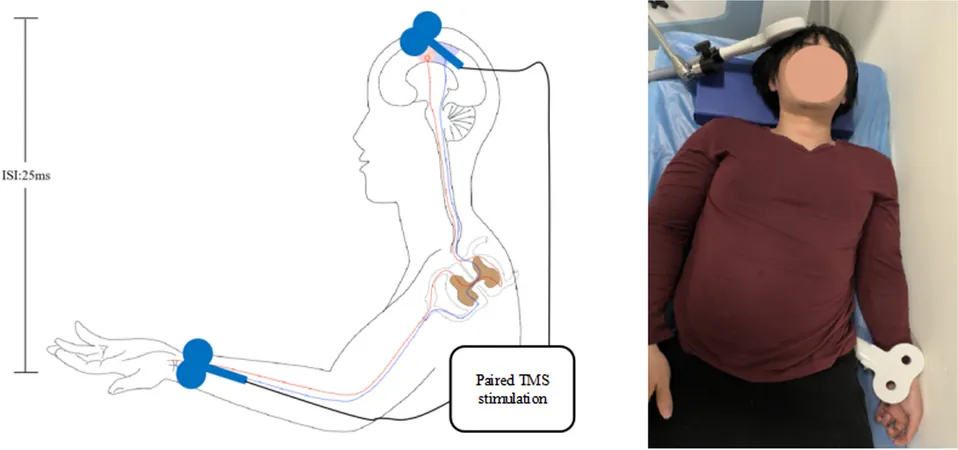
Innovative Methodology
The study is designed as a single-center, single-blind, randomized controlled trial, targeting patients displaying upper limb motor dysfunction post-stroke. The primary focus is to assess the efficacy of paired magnetic stimulation techniques by delivering synchronous peripheral and central magnetic stimulation to optimize recovery outcomes. Patients at Brunnstrom stages III–V, typically between three months and one year since their stroke, will be evaluated for motor functionality before and after a three-week treatment intervention, with follow-up assessments at five weeks and three months.
While the central nervous system's excitability can be enhanced by existing therapies like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), they often neglect the vital role of sensory processing in recovery. The high-frequency magnetic paired associative stimulation proposed in this study seeks to fill that gap, utilizing a dual-coil magnetic device capable of precise timing and intensity adjustments to better facilitate targeted neuronal connections.
Expected Outcomes
The primary outcome measure will be the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT), with secondary assessments using neuromuscular and motor function tests including the Fugl-Meyer Assessment-upper limb, Modified Barthel Index, and neuroelectrophysiological evaluations. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy will also be employed to observe changes in sensorimotor cortex activity, providing insights into the underlying neural mechanisms at play.
Importance of Timing and Coordination
The technique under investigation draws from the principles of Hebbian plasticity, which posits that simultaneous activation of neurons strengthens their connections. By timing peripheral and central magnetic stimulation closely, the aim is to create a synchronized stimulation pattern that potentially enhances motor control and promotes functional recovery.
Future Implications for Stroke Rehabilitation
As dual-coil magnetic stimulation equipment gains traction in clinics, the introduction of high-frequency magnetic paired stimulation can redefine stroke rehabilitation, making recovery more affordable and accessible. Enhanced clinical outcomes from this innovative method promise a shift in rehabilitation paradigms, encouraging ongoing research investments into advanced therapy techniques.
With an anticipated trial completion set for April 2024, medical experts hope that findings will establish high-frequency paired associative stimulation as a standard care protocol, eliminating barriers and fast-tracking patient rehabilitation.
Conclusion
As the medical community continues to explore effective interventions for post-stroke recovery, high-frequency magnetic paired associative stimulation represents a beacon of hope. With the potential to revolutionize rehabilitation for countless stroke patients, this research could pave the way toward significantly improved quality of life and independence for those affected by this pervasive condition. Stay tuned as we monitor results from this promising study!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)