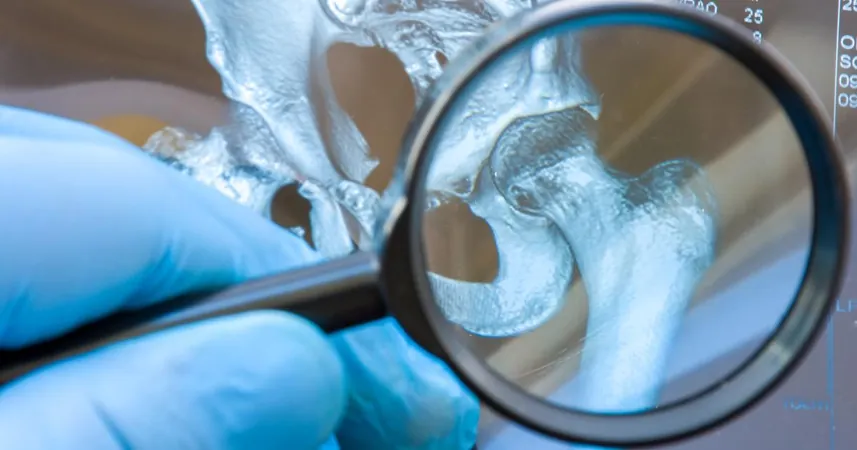

Radiologist Triumphs Over AI in Fracture Detection on X-rays: What This Means for the Future of Medical Imaging
2024-09-23
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study, a radiologist has outshined an artificial intelligence solution in detecting fractures on X-ray scans, highlighting the enduring value of human expertise in medicine. Published in the prestigious journal Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging, the study reveals concerning implications for the implementation of AI in clinical settings.
Background
As emergency departments grapple with an overwhelming influx of patients requiring scans for bone and joint trauma, the traditional X-ray remains the primary diagnostic tool. However, the increase in cases has led to concerns regarding the potential for misinterpretation by healthcare professionals. A striking 2019 report indicated a diagnostic error rate of up to 24% in emergency settings, underscoring the need for reliable solutions.
Study Overview
The study's researchers from France sought to evaluate the efficacy of an AI algorithm named Rayvolve, specifically designed for fracture detection. Utilizing deep learning technology, the AI operated with a sensitivity of 82% and specificity of 69%. Yet, these metrics paled in comparison to the results achieved by a trained radiologist, who recorded a remarkable sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 88%. These findings support the argument that AI tools must complement, rather than replace, human specialists in radiology.
Expert Opinion
Maxime Pastor, a key figure in the study with the Department of Medical Imaging at Nîmes University Hospital, stated, “Our results reinforce the assumption that AI must be monitored. The significant number of false positives and false negatives underscores the irreplaceable role of radiologists in accurately reading X-rays for detecting fractures in adults.”
Methodology
The retrospective analysis included a sample of 94 adult patients suspected of having bone fractures, all of whom underwent both standard CT exams and radiographs at the hospital from 2022 to 2023. AI was tasked with locating fractures, while the radiologist’s interpretations were compared against a reference standard established by senior radiologists interpreting CT scans.
Results
Among the 94 patients, 47 were confirmed to have fractures identified through the CT scans. Of note, the sample revealed a variety of fractures, including 25 in the hand/wrist, 16 in the pelvis, and 30 in the foot or ankle. The AI's analysis identified 58 true positives, 13 false negatives, 33 true negatives, and 15 false positives. In contrast, the radiologist detected 65 true positives, with only 6 false negatives, 42 true negatives, and 6 false positives, showcasing superior performance in sensitivity and accuracy at statistically significant levels.
Discussion
While the study provides valuable insight, it does carry limitations due to its single-center design and limited patient sample size. The authors also remarked that utilizing CT as a reference provided a robust basis for assessing fracture presence, which may explain the AI's comparatively poorer performance compared to previous studies that employed radiographs interpreted by specialist radiologists.
Future Implications
This raises an intriguing possibility: "Should we consider replacing traditional radiographs with ultra-low-dose CT scans?" asked Pastor. This method could offer enhanced diagnostic information and greater certainty, particularly for extremity fractures. The current findings warrant further exploration into AI performance against stronger reference standards, paving the way for improved accuracy in fracture detection.
Conclusion
As the medical field moves toward integrating artificial intelligence more extensively, this study is a critical reminder that while AI can assist, it is the combination of machine learning and human expertise that ultimately benefits patient care. The future of medical imaging holds exciting potential, but these results affirm the essential role of radiologists in ensuring accurate diagnoses.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)