Revolutionizing Heart Health: AI Eye Scans Could Identify Risks for Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke!
2025-04-01
Author: Nur
In an exciting breakthrough, a recent study has demonstrated the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in revolutionizing cardiovascular disease screening through non-invasive eye scans conducted in primary care settings.
Published in the esteemed journal npj Digital Medicine, this pioneering research explores the effectiveness of AI-powered retinal scans as a screening tool for identifying patients at risk of heart attacks and strokes.
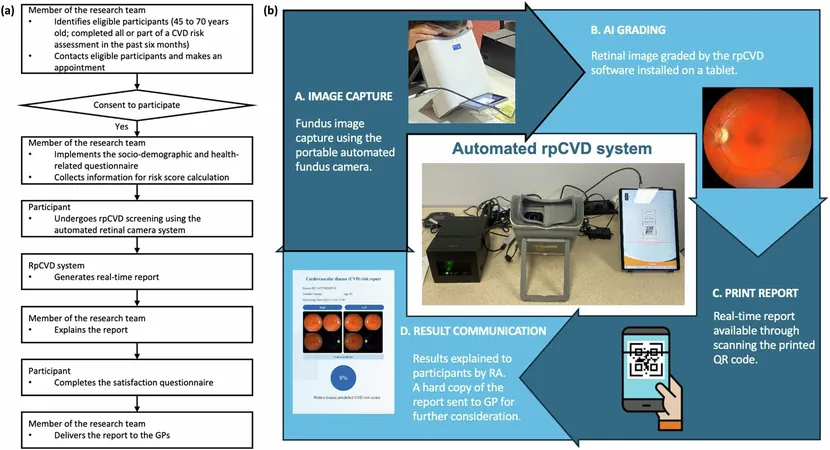
The study, led by Wenyi Hu from the University of Melbourne’s Centre for Eye Research Australia (CERA), underscores the remarkable ease with which this technology can be integrated into the daily operations of general practice clinics. "The retinal camera is simple to use, and both doctors and patients responded positively to its implementation,” Hu stated. She emphasized that future improvements are necessary, particularly for specific demographics, such as men over the age of 60, to enhance the accuracy of the scans.
Study Overview
The research involved 361 participants, aged between 45 to 70 years, who had recently undergone cardiovascular risk assessments at two general practitioner (GP) clinics. Utilizing a desktop retinal camera, the study captured images of the blood vessels at the back of the eye and generated real-time reports predicting cardiovascular disease risk. These results were then compared to the World Health Organization's clinical risk tool, which evaluates factors like age, sex, lifestyle habits, blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol levels.
Remarkably, the findings reveal a significant link between retinal image analysis and traditional risk assessment methods. With data validation from over 27,500 records in the UK Biobank, the AI-generated scores were found to correlate closely with the WHO risk evaluations, indicating a comparable accuracy in forecasting heart disease and stroke risks over a decade.
Among the results, the study highlighted:
- A moderate alignment between retinal scan predictions and WHO risk scores, with a 67.4% match rate.
- A 93.9% success rate in obtaining usable retinal scans for risk assessment.
- High levels of satisfaction, with 92.5% of patients and 87.5% of participating GPs expressing their approval of the technology.
Expert Perspectives and Future Potential
Dr. Malcolm Clark, a participating GP in the study, is optimistic about the transformative potential of retinal scanning in enhancing cardiovascular assessments across Australia. He envisions a future where patients receive automated reminders for eye scans, which would streamline follow-up processes for further testing if necessary. "This could become as routine as cervical screening tests or fecal occult blood tests," he noted.
Associate Professor Lisa Zhuoting Zhu, Hu's supervisor, emphasizes the broader implications of AI-enabled eye scans — not only as a tool for cardiovascular screening but also as a means to gain insights into brain and kidney health. "This advancement could pave the way toward providing cost-effective, scalable, and equitable health care services, particularly for those in remote and underserved communities," she remarked.
As healthcare continues to embrace technological innovations, the integration of AI into routine preventative care represents a crucial step forward, offering hope for improved cardiovascular health outcomes for patients worldwide. With studies like this, we move closer to a future where advanced screening techniques could eventually save countless lives. Stay tuned for more updates on this science-driven journey!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)