Revolutionizing Chikungunya Diagnostics: A New Test for Neutralizing Antibodies Revealed!
2024-09-30
Introduction
The chikungunya virus (CHIKV), transmitted primarily by infected Aedes mosquitoes, leads to recurrent outbreaks marked by severe fever, rashes, muscle pain, and debilitating joint pain. These symptoms are distressingly similar to those of dengue fever, often leading to misdiagnosis in regions where both diseases are active. Presently, the lack of approved antiviral drugs makes accurate and early diagnosis critical for effective management of CHIKV infections.
Current Diagnostic Methods
Current testing methods, such as nucleic acid detection, are only viable during the short viremia phase, approximately seven days post-infection. On the other hand, serological tests like the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) can detect specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies approximately five days into the illness, and immunoglobulin G (IgG) in later stages. However, to truly gauge a patient’s immune status, results from ELISA require confirmation through neutralization tests (NT), which can be impeded by the need for high biosafety level facilities due to the pathogenic nature of CHIKV.
Introduction of Surrogate Virus Neutralization Tests (sVNTs)
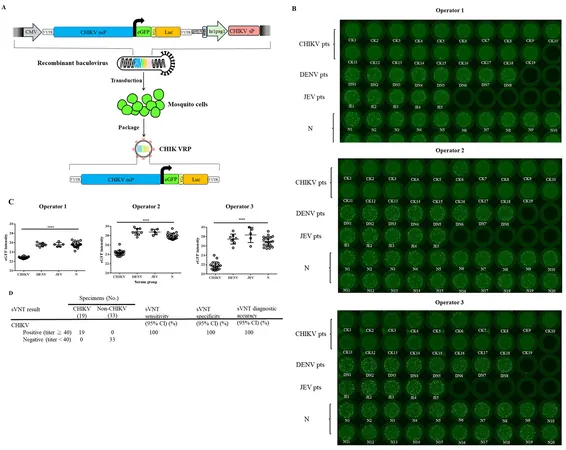
A groundbreaking shift is on the horizon with the development of surrogate virus neutralization tests (sVNTs) derived from mammalian cell culture and pseudotyped viruses. These tests significantly lower safety requirements to biosafety level 2, thus enabling quicker results within 6 to 72 hours. In a recent study, researchers introduced a mosquito cell-derived CHIKV virus-like particle (mos-CHIK VRP) as a promising alternative, enhancing the rapid detection of neutralizing antibodies (nAbs).
Study Results
The study evaluated the effectiveness of the mos-CHIK VRP VNT, which demonstrated 100% sensitivity and specificity in detecting nAbs in a cohort of 52 serum samples. This method stands out for its speed, enabling results within only 20 hours, significantly surpassing conventional approaches. The study showed a tightly correlated quantitative neutralization titer between the new sVNT and standard focus reduction neutralization tests (FRNT), reinforcing its relevance as a diagnostic tool.
Significance and Applications
In essence, the mos-CHIK VRP sVNT promises a versatile utility for estimating the seroprevalence of CHIKV infections, monitoring vaccine effectiveness, and identifying potential disease reservoirs. This innovation isn’t just a technical advancement; it's a crucial leap towards establishing enhanced diagnostics, aiding not only in clinical settings but also in public health surveillance.
Advantages of the New Testing Framework
Key advantages of this new testing framework include:
1. Rapid Turnaround Times
The ability to confirm results within 20 hours could significantly expedite public health responses during outbreaks.
2. High Throughput Capacity
It allows researchers to process large volumes of samples, making it invaluable for extensive seroepidemiological studies.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
The sVNT-eGFP approach is economically viable, minimizing expenses related to reagents and equipment.
Conclusion
The implications of these findings are profound, as understanding the immune landscape of populations can guide future vaccine development and therapeutic strategies against Chikungunya virus. As health officials and researchers work to combat CHIKV, the deployment of this advanced diagnostics tool could prove pivotal in curbing its spread and mitigating the impact of future outbreaks.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)