Revolutionary Virtual Reality Software Reveals Secrets of Pediatric Heart Tumors
2025-07-01
Author: Mei
Groundbreaking Software Changes the Game in Pediatric Oncology
A trailblazing software from Melbourne is set to transform our understanding of the most prevalent heart tumor in children: cardiac rhabdomyoma. This innovative technology, known as VR-Omics, not only sheds light on how these tumors form but could also pave the way for insights into other childhood diseases.
Uncovering the Mysteries of Cardiac Rhabdomyoma
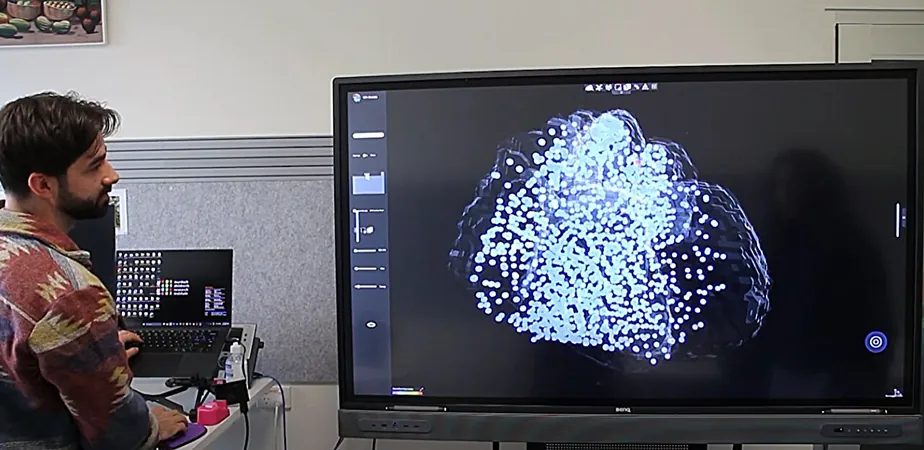
Led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and detailed in Genome Biology, the research highlights VR-Omics' ability to detect previously unnoticed cell activities associated with these benign tumors. Developed by Professor Mirana Ramialison, this revolutionary tool uniquely analyzes and visualizes medical data in immersive 2D and 3D virtual reality formats.
Understanding the Impact and Risks of Cardiac Rhabdomyoma
Detectable in either pregnancy or infancy, cardiac rhabdomyomas are usually harmless. However, some cases can escalate, blocking blood flow and leading to critical health issues like respiratory distress and heart failure. As Professor Ramialison notes, severe cases sometimes necessitate surgical intervention, which carries significant risks.
Pioneering Research that Reveals Hidden Features
To test the capabilities of VR-Omics, Professor Ramialison and her team meticulously analyzed cardiac tissue samples from three children diagnosed with the tumor. Their groundbreaking work exposed specific cellular characteristics of cardiac rhabdomyoma that had previously gone unnoticed.
A Leap Forward in Disease Understanding
"VR-Omics produces intricate 3D visualizations of cellular structures based on extensive patient datasets," explained Professor Ramialison. This leap in technology facilitates a more detailed examination of human tissue than traditional methods allow.
Setting a New Standard in Medical Research
When benchmarked against existing advanced techniques, VR-Omics outperformed competitors at every analytical step. Professor Ramialison emphasizes its exceptional ability to scrutinize vast datasets, uncovering new biological mechanisms in rare tissue samples like those from cardiac rhabdomyoma.
Collaborative Research for a Brighter Future
Contributors to this groundbreaking research include experts from several institutions, such as the Melbourne Center for Cardiovascular Genomics and Regenerative Medicine, University of Konstanz in Germany, and Monash University, among others. Together, they are pioneering a path toward more biological discoveries that may enhance our understanding of numerous childhood conditions.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)