Revolutionary Imaging Breakthrough: Mapping Diseases Like Never Before!
2025-07-18
Author: Arjun
A Game-Changer in Medical Research
In a remarkable leap for medical science, researchers from Aarhus University, in collaboration with global experts, have unveiled an innovative new technology that redefines how we analyze tissue samples from patients. This game-changing method promises to extract a wealth of information from routine biopsies, transforming the landscape of disease diagnosis and treatment.
Introducing PathoPlex: The Future of Disease Mapping
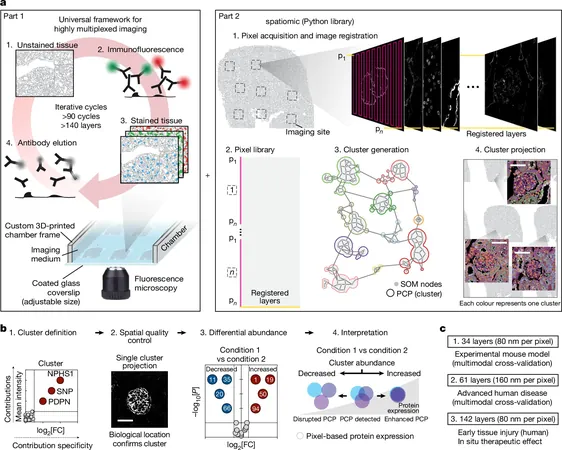
Say goodbye to traditional limitations! The new technique, known as Pathology-oriented multiPlexing or PathoPlex, allows scientists to observe over 100 different proteins within a single tissue specimen simultaneously. Previously, doctors could only examine 1-2 proteins at a time. This extraordinary advancement significantly enhances our understanding of complex diseases.
Recently published in the prestigious journal Nature, PathoPlex utilizes advanced image processing and cutting-edge machine learning to intricately map disease processes.
Spotting Disease Before It's Visible!
One of the standout results of this research involved diabetes patients. Utilizing this revolutionary technology, scientists discovered underlying issues in kidney tissues that were invisible with conventional methods. Professor Victor Puelles from Aarhus University stated, "We were able to observe how diabetes impacts kidney health through a network of simultaneous changes, even identifying alterations in young patients before overt symptoms emerged."
Assessing Medication Effects Directly in Tissues
Perhaps one of the most thrilling applications of PathoPlex is its capacity to evaluate how medications function directly in tissues. In a recent study investigating SGLT2 inhibitors, common diabetes drugs, researchers uncovered unexpected findings. While treatment showed potential benefits in some areas, it also raised critical questions about the need for additional therapies to protect patients' kidneys.
Open to All: A Step Toward Collaborative Science
In a refreshing approach to research, the team has made PathoPlex freely accessible to the scientific community. They have designed scalable options suitable for both small and extensive experiments, including an innovative 3D printer-based liquid handling system. A comprehensive computational guide, along with a Python package dubbed "spatiomic," is available to facilitate image analysis.
"We aimed to provide an open solution that everyone in the research community could utilize," Puelles emphasized.
A Versatile Tool for Diverse Diseases
While the initial study concentrated on kidney diseases, the potential of PathoPlex extends far beyond. Researchers are confident that this technology can be applied across various medical conditions requiring detailed tissue examination, demonstrating its capabilities in liver and brain tissues as well.
The Road Ahead: From Labs to Hospitals
Though this cutting-edge technology promises to revolutionize diagnostics, further work remains to ensure its practical application in hospitals. The research team is committed to automating the method, enhancing benchmarking strategies, and developing concrete clinical applications to benefit patients directly.
This pioneering study is the result of a multinational collaboration involving experts from Germany, Japan, France, the U.S., Australia, and Switzerland, signifying a truly collaborative effort in advancing medical science.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)