Revolutionary Compact Cas9d Enzyme: A Game-Changer in Genome Editing!
2025-09-22
Author: Nur
Breakthrough Discovery in Genome Editing
A groundbreaking study from a research team led by Professor Wang Yanli at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has unveiled the structure and mechanics of a powerful new genome-editing enzyme: Type II-D Cas9, also known as Cas9d. This promising tool holds the potential to transform the field of genetic engineering.
Why Cas9d is the Future of Genome Editing
Traditionally, Cas9 proteins, like the well-known Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 (SpCas9), have dominated the genome-editing scene due to their unmatched cleavage efficiency. However, the bulkiness of SpCas9 limits its effectiveness, particularly in delivering gene edits via adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors. This limitation spurred the urgent need to discover more compact Cas9 variants that retain strong performance.
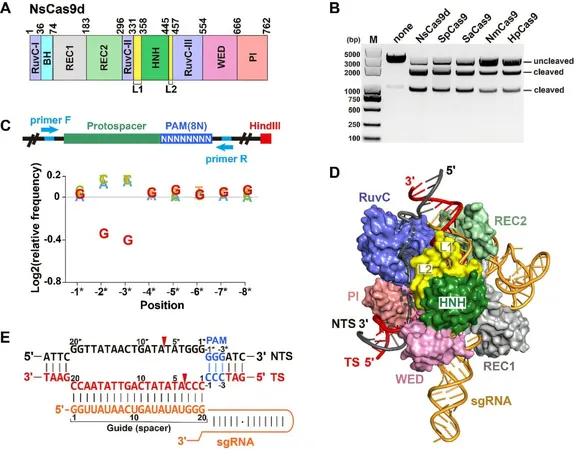
Meet NsCas9d: The Compact Powerhouse!
In their innovative study, the researchers turned their attention to a Type II-D Cas9 derived from a Nitrospirae bacterium, dubbed NsCas9d, which boasts a streamlined structure comprising just 762 amino acids. Utilizing cutting-edge metagenomic datasets, the team successfully identified relevant CRISPR sequences and engineered a specific sgRNA for nsCas9d's operations.
Outstanding Performance in Cleavage Tests
In laboratory tests, NsCas9d demonstrated remarkable performance, requiring only a 20-nucleotide pairing between the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and sgRNA to achieve cutting efficiency on par with SpCas9. This finding takes genome editing to new heights!
The Science Behind the Mechanism
Advanced assays revealed that NsCas9d specifically recognizes a unique PAM sequence, notably the 5'-NRG-3' variant. Among these, the 5'-NGG-3' showed the best cleavage performance in vitro, marking a significant advance in understanding Cas9 function.
High-Resolution Structure Unveiled!
Adding to the excitement, the researchers resolved the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the NsCas9d-sgRNA-dsDNA complex at an impressive 2.86 Å resolution. This groundbreaking achievement is the first to provide a detailed view of the complete HNH and RuvC domain structures for a Type II-D Cas9.
Implications for Future Gene Editing!
Notably, NsCas9d generates 3-nucleotide 5' overhangs as cleavage products, a sticky-end feature that could significantly enhance the efficiency and predictability of DNA repair during gene editing processes, such as insertions. This capability could lead to more precise and effective genetic modifications in various applications.
The Future is Bright for Cas9d!
These findings not only promise advancements in CRISPR technology but also signal a new era in genetic research with applications ranging from medicine to agriculture. The compact Cas9d enzyme is set to revolutionize how we approach genome editing, making it more accessible and efficient than ever before!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)