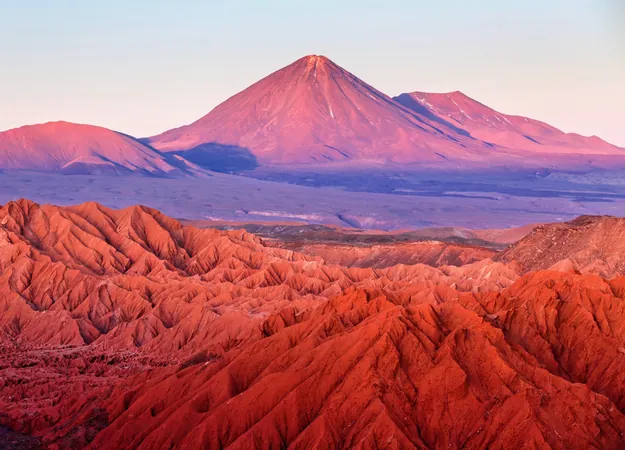

Incredible Microbial Life Discovered in the Harsh Atacama Desert: What Scientists Found Will Astonish You!
2024-11-15
Author: Rajesh
Incredible Microbial Life Discovered in the Harsh Atacama Desert: What Scientists Found Will Astonish You!
Described as a barren and inhospitable landscape, the Atacama Desert in Chile is known as the driest desert on Earth. With its sun-baked terrain and limited moisture, life seems nearly impossible in this arid environment. However, recent research unveiled a remarkable discovery—a thriving community of microorganisms that defy the harsh conditions.
While many would assume that life is scarce in such a desolate place, a groundbreaking study published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology reveals that life not only exists but actively flourishes in these extreme conditions.
Cutting-Edge Technique Unveils Hidden Life
Leading the research was Dr. Dirk Wagner from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam, who introduced an innovative method for differentiating between living and dead microorganisms in soil samples. By meticulously isolating extracellular DNA (eDNA) from intracellular DNA (iDNA), researchers were able to identify actively living microbes that were previously masked among dormant and deceased cells. This technique revolutionizes microbial research, especially in environments where conventional DNA extraction methods fail.
During fieldwork, researchers collected soil samples along a transect extending from the Pacific Ocean to the foothills of the Andes. What they uncovered was astonishing: a rich tapestry of active microorganisms, showcasing how resilient life can be even in the most parched regions of the planet.
The Microbial Pioneers of Aridity
Dr. Wagner elaborated on the significance of these findings, stating, “Microbes are the pioneers colonizing this kind of environment, laying the groundwork for future life forms.” This dynamic implies that similar microbial processes could also occur in terrains that experience geological disturbances, such as earthquakes or landslides, where life might again take root in barren soil.
Implications for the Quest Beyond Earth
The implications of this research stretch beyond our planet. As scientists delve deeper into astrobiology—the study of life in the universe—the newfound techniques for identifying living microbes on Earth can also be applied to extraterrestrial environments. Mars, with its striking similarities to the Atacama’s desolation, offers a tantalizing opportunity. Researchers speculate that potential microbial life could exist underground, waiting to be discovered.
This breakthrough method could significantly enhance the ability of future Mars missions to detect signs of life by identifying microbial remains overlooked by conventional techniques, bringing us closer to understanding whether we are alone in the universe.
Expanding Research Frontiers
The study spearheaded by Dr. Wagner opens exciting new avenues for research not only in the Atacama Desert but also in other extreme ecosystems—such as Antarctic terrains, deep-sea vents, and other arid regions worldwide. By unlocking the secrets of these resilient microorganisms, scientists can better grasp their roles in nutrient cycling, climate change dynamics, and broader biogeochemical processes.
As the resilience of life in extreme environments is unveiled, we stand on the brink of expanding our knowledge of microbial life's limits and capabilities. Dr. Wagner’s commitment to exploring these techniques in various hostile contexts will undoubtedly illuminate the secret lives of microbes and their significance.
A New Paradigm in Microbial Ecology
With this research, the understanding of microbial ecology is undergoing a paradigm shift. By painting a clearer picture of life that thrives in the harshest conditions, scientists are not only addressing intrinsic questions about survival but also entering a fascinating realm wherein life on Earth and potentially elsewhere in the universe might be connected.
The Atacama Desert, long perceived as a lifeless void, is now seen as a vibrant ecological frontier. The ongoing research represents a crucial step in unraveling the mysteries of life, giving humanity hope for future discoveries that could redefine our understanding of survival and resilience across planets. Keep your eyes peeled for more astonishing findings from this extraordinary research!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)