Incredible Discovery: New Satellite Unveils Hidden Geological Features Under the Ocean that Could Transform Our Understanding of Earth!
2025-01-01
Author: Rajesh
Groundbreaking Revelation from NASA's SWOT Satellite
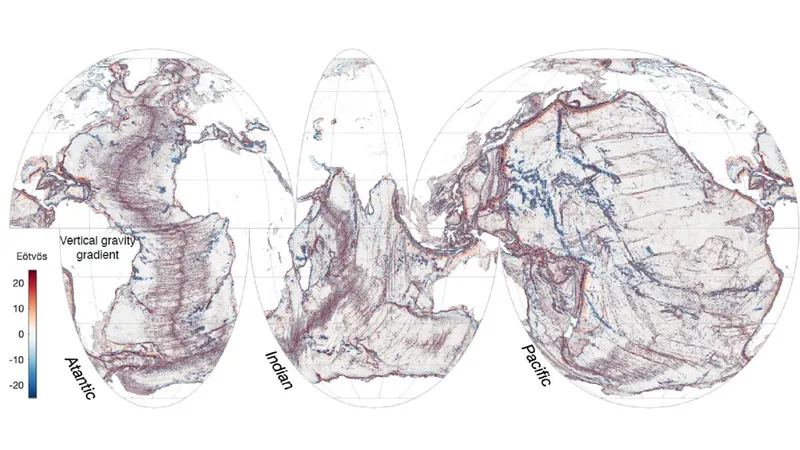
A groundbreaking revelation by scientists has emerged from the first-year findings of NASA’s revolutionary Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite. Launched in December 2022 in collaboration with France’s Centre National D’Études Spatiales, this state-of-the-art satellite has meticulously mapped the ocean floors of our planet with unprecedented clarity, unveiling vital underwater features that could reshape scientific theories.
Unprecedented Clarity in Ocean Topography
According to the study published in the esteemed journal Science, the SWOT mission has managed to provide a clearer depiction of ocean topography than what was achieved in three decades through traditional ship voyages and older satellite technologies. Utilizing advanced measurements with an impressive 5-mile (8-kilometer) resolution, this satellite has provided more information in one year than was previously accessible.
Enhancing Scientific Understanding of Tectonic Theories
"The remarkable detail we’ve captured will deeply enhance scientific understanding, particularly concerning tectonic theories," stated Yao Yu, a physical geographer at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and co-author of the study. The insight gained from these findings stands to advance our knowledge of ocean currents, nutrient transport, and the geological history of Earth’s oceans.
Innovative Methodology of SWOT
SWOT's innovative methodology measures subtle variations in ocean surface heights caused by gravitational pulls from underwater structures. “The ocean surface may seem flat, but it’s shaped by the hidden hills and volcanoes below,” Yu explained. This means that fluctuations in sea surface height can be indicators of geological features lying deep beneath the waves.
Focusing on Primary Underwater Structures
The research team concentrated on three primary underwater structures: abyssal hills, small seamounts (underwater volcanoes), and continental margins. Abyssal hills, which are just hundreds of feet in height, are formed by tectonic plate movements. The SWOT data revealed individual hills and highlighted changes in ridge directions, hinting at past shifts in tectonic activity that shaped these underwater features.
Discovery of Numerous Abyssal Hills and Seamounts
Surprisingly, researchers discovered a multitude of abyssal hills in a disturbingly short period, a finding that intrigued Yu. In addition, they identified thousands of smaller seamounts—underwater volcanoes that are crucial for understanding ocean currents and biodiversity—measuring less than 3,300 feet (1,000 meters) tall, many of which were previously unidentified.
Refining Understanding of Coastal Ecology
This detailed mapping has also allowed the team to refine their understanding of tectonic boundaries and ocean currents, especially in coastal areas where nutrient and sediment transport from land plays a pivotal role in influencing marine biodiversity and ecosystems. “We are particularly interested in continental margins due to their significant impact on coastal ecology,” Yu added.
Implications for Future Research
As we continue to explore the mysteries of our planet's oceans, this study opens the door to future research that could not only enhance our geological knowledge but may also lead to new understandings of how underwater ecosystems thrive. With such groundbreaking data, scientists are now more than ever equipped to tackle the immense challenges posed by climate change and its effects on oceanic habitats.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as this scientific journey unfolds—who knows what other hidden treasures the depths of our oceans might reveal!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)