How Aquarius Helicase Supercharges HIV-1 Integration into Genomic Areas
2025-08-20
Author: Li
Unlocking the Secrets of HIV-1's Integration Strategy
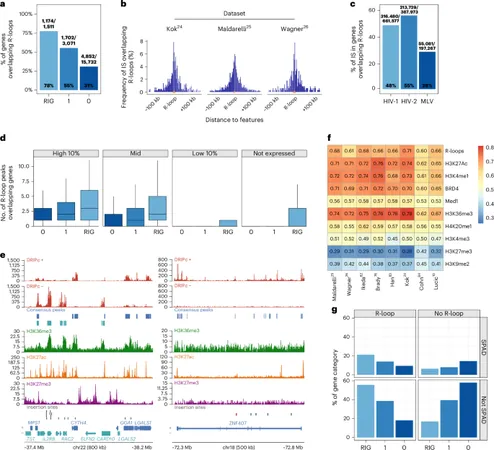
In the ongoing battle against Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1), researchers have made groundbreaking discoveries regarding how the virus integrates into host genomes. One key player—Aquarius helicase—is emerging as a vital facilitator that targets R-loop enriched genomic regions. This intricate process not only enhances viral replication but may offer new avenues for therapeutic strategies.
The Role of R-loops and Aquarius Helicase
Recent studies highlight how HIV-1 preferentially integrates its genome at sites enriched with R-loops—structures formed during the transcription of DNA into RNA. These R-loops create unique environments that favor viral integration, allowing HIV-1 to evade immune responses and persist in the host.
Aquarius helicase appears to play a crucial role in this process. By manipulating RNA structures, it helps guide the HIV-1 genome to these favorable integration sites, thus enhancing the efficiency of viral replication.
Why This Discovery Matters
Understanding the dynamics of HIV-1 integration is pivotal for developing effective treatments. By targeting the mechanisms underpinning the virus's ability to embed itself within the human genome, scientists could devise innovative therapies that disrupt this integration process. In particular, drugs designed to inhibit Aquarius helicase might limit the virus's reproductive capabilities.
The Future of HIV Research
The ongoing research into Aquarius helicase and its interactions with HIV-1 offers hope in the quest for an effective HIV cure. As scientists continue to map the nuclear landscapes affected by this virus, they are uncovering potential pathways for therapeutic intervention, paving the way for strategies to eliminate HIV-1 reservoirs in infected individuals.
This groundbreaking work emphasizes the critical need for continued research in virology and genetics. With every finding, we move one step closer to overcoming the challenges posed by HIV-1, potentially transforming the future of treatment and cure.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)