Grounded Running: The Energy-Saving Secret of Emus and Its Evolutionary Roots
2024-09-26
Introduction
A fascinating study involving a small team of biologists and animal movement specialists from the Netherlands and the U.K. has brought to light how birds like the emu utilize a unique grounded running style at medium speeds—an adaptation that enables them to conserve energy more efficiently than other bipedal animals, including humans.
Study Overview
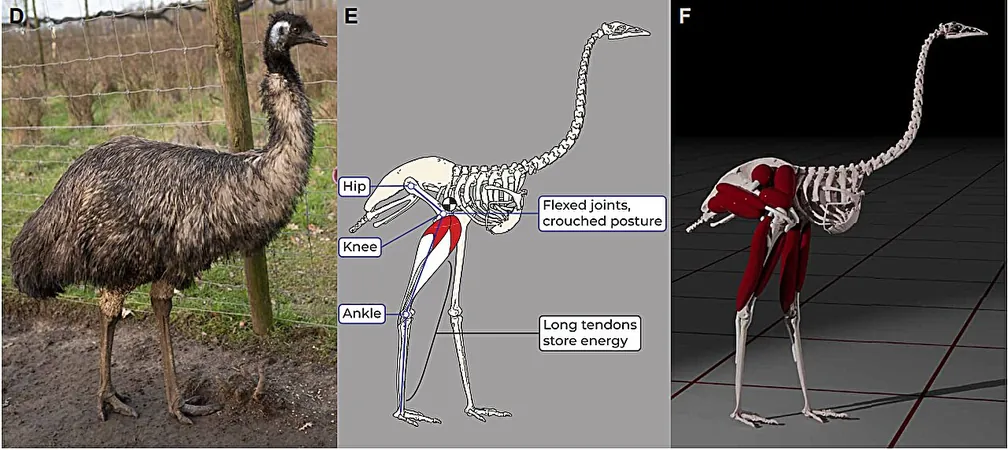
Published in the journal Science Advances, the research focused on emus to understand the mechanics of their running style. Unlike humans who leap into the air with each step, emus maintain at least one foot on the ground while running at moderate speeds, which significantly reduces their energy expenditure.
Research Methodology
The research team meticulously simulated the emu's running style using a digital marionette constructed from artificial muscles, bones, and tendons. This innovative model allowed the researchers to adjust the rigidity of the tendons, effectively mimicking the emu's running mechanics. After successfully teaching their creation to walk, the team pushed it to run with minimal energy usage, which resulted in a strikingly accurate imitation of the grounded running style observed in actual emus.
Key Findings
Key findings in the study suggest that the emu's anatomy plays a crucial role in its running capabilities. The evolutionary adaptations that have occurred over time restrict the bird's legs from fully straightening, making the grounded style more energy-efficient at intermediate speeds. This anatomical feature is thought to have its origins in non-avian dinosaurs, indicating that such a running style may have deep evolutionary roots.
Implications of the Study
As a result, this remarkable energy-saving mechanism could offer insights into the locomotion of other species and inform future research on the biomechanics of motion. The implications extend beyond birds, prompting a reevaluation of how different animals have adapted their movement strategies in response to their environments and physical constraints.
Conclusion
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, understanding these natural energy-saving strategies could inspire innovative solutions in various fields, including robotics and biomechanical engineering. Will we soon see advances in technology that mimic nature's genius? Only time will tell! Keep an eye on future research for more discoveries that could revolutionize our understanding of movement across the animal kingdom!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)