
Shocking Cricket Behavior: How Hunger Alters Mating Choices!
2024-09-25
Introduction
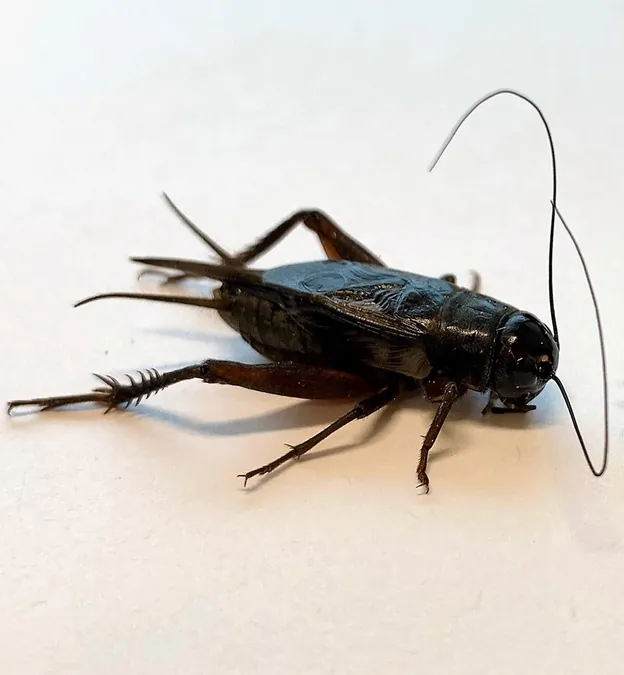
A groundbreaking study from biologists at the University of Minnesota has revealed fascinating insights into the mating behaviors of male Pacific field crickets.
Research conducted by Jon Richardson, Isabelle Hoversten, and Marlene Zuk suggests that when these male crickets are low on energy, they tend to focus their mating interests exclusively on females, effectively narrowing their mating filter.
Study Findings
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study investigates how energy levels influence the mating decisions of male crickets.
Previous research has often overlooked same-sex sexual behavior (SSB) in animals, leading to a lack of understanding about its prevalence and significance across species.
Interestingly, SSB has been observed in various creatures in natural environments, raising questions about its functions and evolutionary advantages.
Research Methodology
The researchers concentrated on the mating behaviors of male Pacific field crickets, well-known for courting both males and females.
The study monitored their courtship songs, a key factor in attracting female crickets.
It has been established that females are more inclined to mate with males who produce high-quality songs. Hence, mate selection becomes paramount, especially under energy constraints.
Experimental Setup
In their experiments, male crickets were divided into two groups: one with an unrestricted, well-fed diet and the other on a restricted calorie diet.
Each group was then introduced to crickets on a regular diet, providing the opportunity to test their mating preferences.
Results and Implications
The results were striking. The hungry male crickets demonstrated a significant decrease in attempts to mate with other males, showcasing their narrowed focus due to energy limitations.
However, no changes were noted in their efforts to court females, and the well-fed crickets displayed consistent mating behaviors regardless of their partners’ conditions.
Conclusion
This research not only sheds light on the complexities of animal behavior but also poses intriguing questions about survival strategies in the animal kingdom.
The decision-making process of these crickets, shaped by their energy needs, invites parallels to human behaviors related to resource availability and social dynamics.
As scientists continue to explore these intricate behaviors, one thing is clear: even in the animal world, the struggle for energy impacts love and attraction in profound ways.
What other surprises lie in the world of animal dynamics? Stay tuned for more astonishing discoveries!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)