Groundbreaking Study Reveals Crucial Insights into Children's Immune Dysfunction During Severe Infections
2024-09-23
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study conducted by a consortium of researchers from King's College London, Imperial College London, and the University of Edinburgh, important information has emerged regarding the immune system of children suffering from severe infections and inflammatory diseases. This significant research, recently published in *Nature Communications*, aims to enhance the treatment protocols for immune system disruptions that can pose life-threatening risks to children.
Understanding Immune Dysfunction
Severe infections and inflammatory diseases, often identified by fever and commonly referred to as febrile illnesses, can severely impair the immune system's ability to function effectively. This phenomenon, termed "immune dysfunction," not only hampers the body's ability to fight off infections but can also lead to an overactive immune response, potentially causing harm to healthy tissues.
Challenges in Diagnosis
One of the major challenges in treating febrile illnesses is the similarity of symptoms across various conditions. Illnesses such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome of childhood (MIS-C), which has been associated with COVID-19, severe bacterial infections, severe viral infections, and Kawasaki disease often present overlapping symptoms, complicating timely and accurate diagnosis. Understanding the nuances of immune responses in relation to different febrile illnesses could be crucial for improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment strategies.
Research Findings
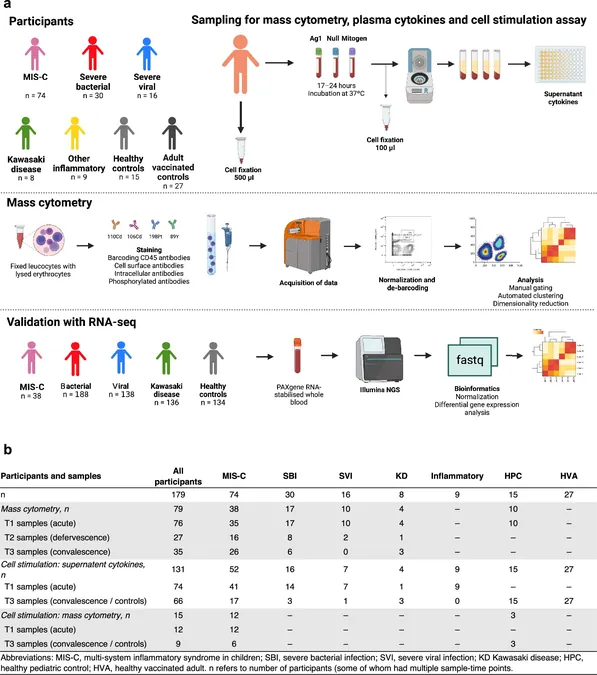
The research team analyzed blood samples from 128 children diagnosed with diverse febrile conditions, tracking the immune cell profiles over the illness duration. Notably, they discovered that children with MIS-C and severe bacterial infections exhibited similar immune profiles, despite the distinct origins of these diseases. Dr. Michael Carter, co-lead author of the study, remarked, "The immune responses in cases of severe bacterial infections and MIS-C were unexpectedly similar, highlighting a critical area for further investigation."
Technological Methods
Advanced technologies such as mass cytometry and immunoassays allowed the researchers to identify distinct groups of white blood cells, particularly neutrophils and T cells, that were significantly disrupted in these children. They also noted that levels of interferons, vital proteins responsible for viral clearance, were substantially decreased in those suffering from severe viral infections.
Impact of COVID-19
This research came at a crucial time, as the COVID-19 pandemic led to an alarming increase in hospital admissions for children exhibiting symptoms reminiscent of severe bacterial infections, including high fevers, conjunctivitis, and rashes. However, many of these cases turned out to be MIS-C, arising roughly four weeks post-COVID-19 infection.
Conclusion
As this study uncovers the complexities of immune dysfunction in the pediatric population, it paves the way for targeted treatments that could drastically improve outcomes for children facing severe infections and inflammatory diseases. The findings not only enhance our understanding of pediatric immunology but also underscore the urgent need for vigilant monitoring and innovative therapies in a post-pandemic era.
Future Directions
Stay tuned for further developments as the scientific community dives deeper into this vital research area, ensuring that no child's health is compromised in the future.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)