Groundbreaking Research Unravels the Secrets of Ice Sheet Melting and Its Impact on Sea-Level Rise!
2024-11-04
Author: Nur
Groundbreaking Research Unravels the Secrets of Ice Sheet Melting and Its Impact on Sea-Level Rise!
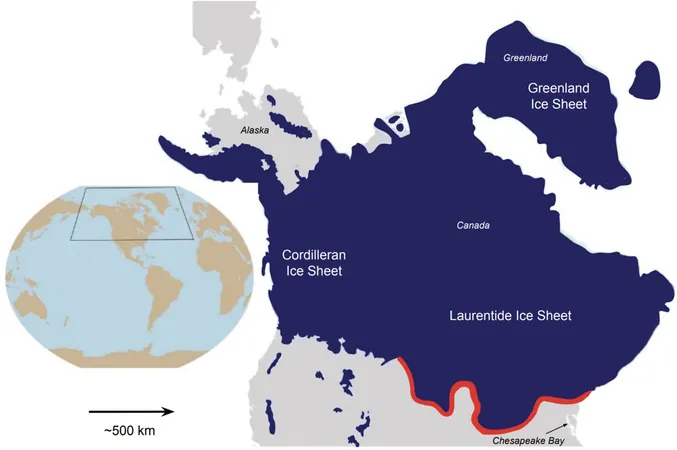
Imagine a colossal ice sheet blanketing Canada and stretching over a significant portion of the northern United States, creating a scene reminiscent of icing gracefully cascading down a cake. This icy expanse existed between 19,000 and 26,000 years ago, reaching as far south as modern-day Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, and Wisconsin.
But what happened after that ice sheet melted, and why should we care? The answer lies in understanding how this melting affects present-day sea levels and contributes to land subsidence.
Ph.D. candidate Karen Williams has taken on the challenge of uncovering these secrets through her innovative computer modeling research. Collaborating with her mentor, Associate Professor D. Sarah Stamps from the Department of Geosciences, as well as esteemed colleagues Daniele Melini from the Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia in Italy and Giorgio Spada from the Università di Bologna, their ground-breaking findings recently made headlines in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth.
The Ups and Downs of Melting Ice: A Closer Look
Williams' computational models assessed the effects of the Laurentide ice sheet's melting on contemporary vertical land movements. Through nearly 130,000 simulations, she explored how different factors—such as the Earth's internal structure—could impact current conditions.
The shocking results showed a pattern of downward movements in the eastern United States, leading to a relative rise in sea level. Conversely, eastern Canada experienced uplifting movements, which resulted in a relative drop in sea levels. How could this be possible?
Unpacking the Mystery of Land Elevation
Understanding why certain regions are sinking while others are rising reveals important insights. As Williams explains, "By obtaining more accurate model estimates related to land rising or sinking, we can pinpoint areas that are experiencing localized vertical displacements due to both natural and human-induced factors." For instance, excessive groundwater extraction in regions like the Gulf of Mexico and Chesapeake Bay has a significant role in these variations.
Stamps elaborates further, noting that, "Significant discrepancies between our models and observed realities often occur in places with known groundwater extraction, such as Houston, Texas." This information could prove crucial for cities grappling with the consequences of their water management decisions.
Aiding Community Planning Efforts
The implications of this research extend beyond academia. The results will pave the way for detailed mapping and resources that will inform policymakers and communities about managing their aquifers effectively. Williams emphasizes the ultimate goal: "Our research will contribute to a comprehensive report for the U.S. Geological Survey, empowering stakeholders in the Chesapeake Bay area to grasp the financial, ecological, and social ramifications of rising sea levels."
As our planet continues to change, understanding the intricate dance between melting ice sheets and land movement will be key to safeguarding communities against the relentless tide of sea-level rise. Stay tuned for further developments, as this research could reshape our approach to climate resilience!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)