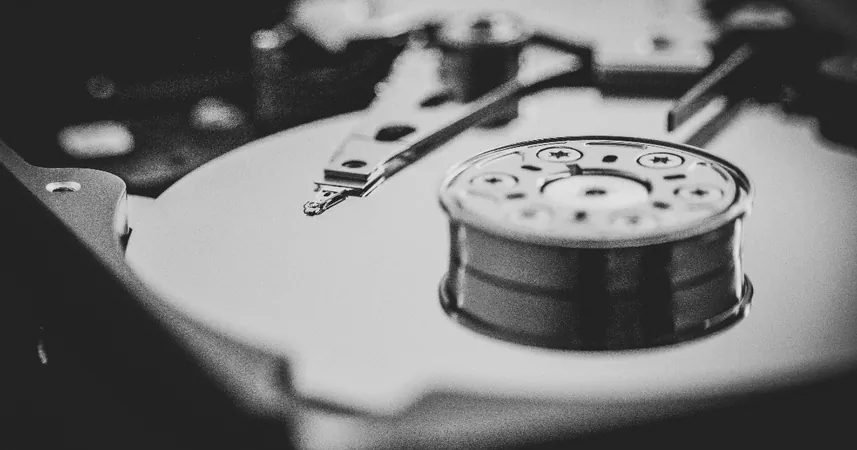

Google Cloud's Game-Changer: Introducing HDD Tier for Spanner Database Slashes Cold Storage Costs by 80%!
2025-03-22
Author: Wei
Introduction
In a groundbreaking move, Google Cloud has unveiled a tiered storage solution for its acclaimed Spanner distributed SQL database, and it comes with an astonishing 80% reduction in costs for cold storage! This new HDD (Hard Disk Drive) option not only optimizes expenses for seldom-accessed data but also simplifies the traditional data migration processes that many companies struggle with.
Traditional SSD Tier
Traditionally, Spanner’s default SSD (Solid State Drive) tier caters to datasets that demand high-performance access, boasting rapid throughput and minimal latency. However, the new HDD tier targets larger datasets that are rarely used or do not require the same swift response times. This strategic tiering is conducted through policy-driven automation, allowing data to be seamlessly transitioned from SSD to HDD without the hassle of manual interference.
Operational Relevance and Cost-Effectiveness
Google's experts have noted a significant trend: as database records age, their immediate operational relevance tends to decrease, even as their importance for reporting and compliance grows. This means businesses are increasingly recognizing the need for budget-friendly storage solutions for archived data, steering clear of the prohibitive costs associated with fast-access SSD storage.
Migration Challenges
Matthew Muckloo, a software engineer at Google, along with Piyush Mathur, a group product manager, emphasize the challenges that often accompany migrating to different storage types. They explain that notoriously complicated data pipelines can disrupt operational performance, often leading to inconsistent data reads and necessitating cumbersome application-level reconciliations.
Flexible Storage Policies
With this innovative update, storage policies can be implemented at multiple Spanner levels—be it database, table, column, or secondary index—affording users the flexibility to allocate specific data types to more economical HDD storage. For instance, less frequently accessed information, like JSON product attributes, can now be efficiently transferred to HDDs, while keeping critical indexes on speedy SSDs.
Activating Tiered Storage
To activate tiered storage, users need to define a locality group that specifies their chosen storage options. For example, by setting a local group with an SSD to HDD spill policy, data can be retained on SSD for a predetermined period—say 15 days—before transitioning into the more cost-effective HDD space.
Comparative Advantages
While Google Spanner is not the only player in the distributed cloud database arena to offer tiered storage solutions, it stands out for its seamless integration and adaptable frameworks. Competing service providers, like Amazon DynamoDB, may shield their storage technology behind layers of abstraction, complicating direct comparisons.
Conclusion
As organizations continue to grapple with data management challenges, Google Cloud's introduction of the HDD tier could be the much-needed solution for businesses aiming to trim costs and optimize their data handling strategies. Stay tuned as we explore more innovations that shape the future of cloud computing!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)