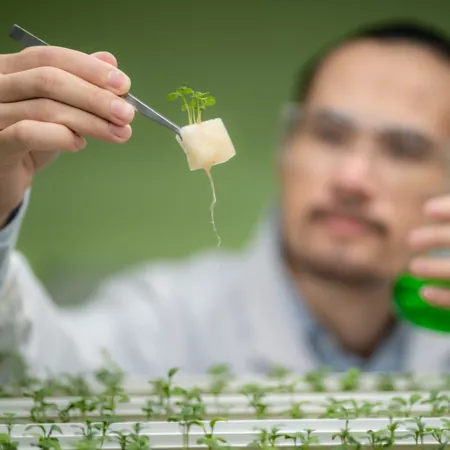

Golden Lettuce: A Breakthrough in Boosting Pro-Vitamin A Content for Healthier Eating
2024-09-23
Introduction
Recent advancements in plant biotechnology have led researchers to discover a groundbreaking method to enhance the beta-carotene content in plant leaves by up to 30 times. Utilizing biotechnological techniques in conjunction with treatments involving high light intensity, this innovative approach not only increases the vital carotenoid levels but also preserves essential processes, including photosynthesis.
Importance of Beta-Carotene
Beta-carotene, an important carotenoid and pigment found in plants, is renowned for its numerous health benefits. It serves as a precursor to retinoids—chemical compounds crucial for various bodily functions such as vision, immune response, and cell growth and differentiation. With the research conducted on tobacco plants (Nicotiana benthamiana) and replicated in lettuce (Lactuca sativa), the implications for improving nutritional content in crops are significant.
Research Insights
Lead researcher Manuel Rodríguez Concepción from the Institute for Plant Molecular and Cell Biology in Valencia, Spain, explains that carotenoids like beta-carotene are essential for the chloroplasts in leaves to function correctly. Excessive or insufficient production of beta-carotene can disrupt chloroplast activity, eventually leading to leaf death. His team's successful manipulation of beta-carotene accumulation in new cellular compartments represents a significant leap forward in agricultural biotechnology.
Storage and Bioaccessibility
The findings, published in *The Plant Journal*, reveal that high concentrations of beta-carotene can be stored in unusual places, such as plastoglobules and fat storage vesicles, rather than being confined solely to photosynthetic complexes. By stimulating the formation of these structures through molecular techniques and intense light exposure, not only does the study enhance the accumulation of beta-carotene, but it also improves its bioaccessibility—the ease of extraction and absorption into the human digestive system.
Nutritional Implications
This breakthrough in biofortification has the potential to significantly improve nutrition by enhancing the beta-carotene levels in crops such as lettuce, chard, and spinach, all while maintaining their natural flavor and aroma. The research team found that when beta-carotene synthesis occurs in plastoglobules combined with production outside of chloroplasts, there is a remarkable 30-fold increase in accessible beta-carotene levels, giving the lettuce leaves a vibrant golden hue.
Global Health Context
Addressing a pressing global health issue, vitamin A deficiency affects a substantial percentage of populations worldwide. Studies suggest that 56% of preschool-age children and 69% of non-pregnant women of reproductive age are deficient in at least one of the three core micronutrients: iron, zinc, and vitamin A. Vitamin A and zinc are particularly vital for maintaining eye health and overall wellbeing.
Ongoing Discussions and Controversies
This research resonates with ongoing discussions about bioengineered crops aimed at combating nutrient deficiencies. Earlier this year, attention was drawn to the controversial “golden rice,” a genetically modified variety designed to combat vitamin A deficiency in developing regions. Despite gaining approval for commercial cultivation in the Philippines, this initiative faced criticism over the genetic modification process and the associated health concerns.
Regulatory Developments
In response to these developments, authorities such as the European Food Safety Authority have revised their guidelines on vitamin A and beta-carotene intake, suggesting the need for careful regulation especially among vulnerable populations such as infants and adolescents.
Conclusion
These innovative advancements in enhancing beta-carotene levels in crops could revolutionize dietary options, presenting an exciting new avenue for tackling global malnutrition and promoting healthier eating habits. The quest for more nutrient-dense crops continues, promising a brighter and healthier future for many.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)