Breakthrough Model Predicts Listeria Growth in Artisanal Cheeses – Could Your Favorite Cheese Be at Risk?
2025-04-01
Author: Jia
Introduction
Listeriosis is a serious public health concern, classified as one of the most dangerous zoonotic foodborne diseases. Despite the relatively few cases reported annually, the potentially high mortality rate associated with Listeria makes understanding its proliferation essential, especially in foods that are consumed without any cooking or heat treatment.
Research Development
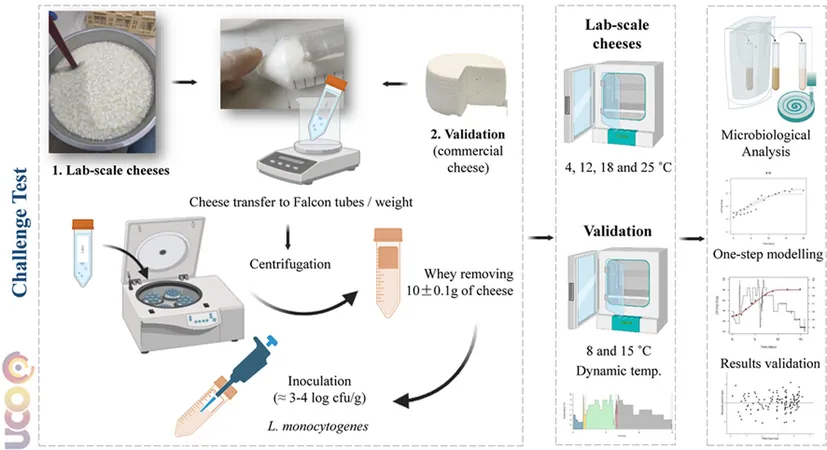
In an exciting development, a research team from the Department of Bromatology and Food Technology at the University of Cordoba has created a groundbreaking mathematical model that accurately predicts the growth of Listeria in artisanal fresh cheeses. This advancement not only helps estimate the shelf life of these food products but also assesses how different storage conditions can affect bacterial growth.
Focus on Goat Milk Cheeses
This research, showcased in the journal Food Control, particularly focuses on artisanal fresh goat milk cheeses. These cheeses are known to have been implicated in multiple listeriosis outbreaks in recent years, highlighting their status as Ready-to-Eat Foods (RTEFs). RTEFs require no additional cooking and are consumed straight from their packaging, making them potentially risky if contaminated.
Storage Temperature Evaluation
Lead researcher Olga Bonilla explained that the team evaluated various storage temperatures—specifically at 4, 12, 18, and 25 degrees Celsius—using predictive microbiology techniques to determine how long it takes for the bacteria to reach legally permissible concentration limits in contaminated cheeses. Alarmingly, their findings indicate that freshly made goat milk cheese could exceed regulatory safety limits within just four days in refrigeration at 4 degrees Celsius.
Limitations of the Model
While the model provides crucial insights, Bonilla cautioned that these findings are specific to the tested conditions and should not be generalized to all cheese types. Each variety has unique characteristics that necessitate specific validation of the growth model, including factors like manufacturing processes, storage conditions, ingredient composition, and pH levels.
Practical Applications
Co-author Antonio Valero emphasized the model's practical application, stating that it empowers producers to demonstrate the safety of their products against Listeria contamination by applying their specific production practices and scientifically estimating shelf life. This is particularly vital in light of recent changes to European Union regulations, which have tightened food safety standards regarding Listeria control.
Collaborative Effort
The collaborative effort known as HIBRO at the University of Cordoba also included contributions from institutions in Portugal, Morocco, and Egypt, showcasing international cooperation in the fight against foodborne pathogens.
Conclusion
With this new predictive model, both producers and consumers of artisanal cheeses can navigate the complex landscape of food safety more confidently—ensuring that that delicious cheese on your table is not only enjoyable but also safe to eat!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)