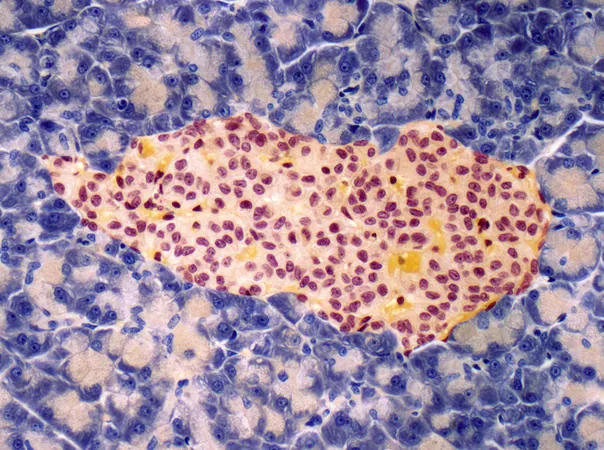
Breakthrough in Beta Cell Transplantation: A Gender-Specific Strategy Boosts Survival Rates!
2025-06-24
Author: Jia
Revolutionary Insights from Weill Cornell Medicine!
In an exciting leap forward for type 1 diabetes treatment, a study from Weill Cornell Medicine has discovered a groundbreaking method to enhance the survival of transplanted beta cells. Titled "ChemPerturb-seq screen identifies a small molecule cocktail enhancing human beta cell survival after subcutaneous transplantation," this research reveals how sex-specific approaches can significantly improve outcomes.
A Tailored Approach: Surprising Gender Differences!
Using a novel chemical screening tool called ChemPerturb-seq, researchers identified a powerful small molecule cocktail that markedly improved the function of pancreatic islets in female mice. However, in a shocking twist, this same treatment did not yield the same benefits in male mice. Dr. Shuibing Chen, the study’s senior author, noted, "We found a clear difference between male and female animals regarding islet survival and functionality after treatment."
The Power of AI in Medical Research!
The LIP mixture—a trio of beta-lipotropin 61-91, insulin growth factor (IGF)-1, and prostaglandin E2—was initially successful in females but fell short for males. Undeterred, the research team leveraged their AI-driven platform to discover that adding two hormones, serotonin and histamine, could bridge the gap. This enhancement allowed the treatment to perform well in male mice as well.
Understanding the Biological Battle Against Diabetes!
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system wreaks havoc on insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leaving patients reliant on insulin therapy for life. Despite the FDA's recent approval of Lantidra, the first islet cell therapy product, a staggering up to 60% of transplanted cells can perish within days. Traditional methods of delivering these cells to the liver pose significant risks, making the search for safer alternatives crucial.
Next-Level Research Tools!
Graduate student Jeya Vandana innovated by combining chemical screening with single-cell RNA sequencing, leading to the development of the ChemPerturb-seq platform. This powerful tool enables researchers to examine 46 different small molecules in one go, setting the stage for revolutionary advancements in diabetes treatment.
The Future Looks Bright for Diabetics!
The implications of this research are remarkable! The new formulation, termed LIPHS, combines the LIP cocktail with serotonin and histamine to drive islet function in both sexes. Researchers aim to expand their analysis to 300 FDA-approved drugs, potentially unlocking new treatments for diabetes and beyond.
Empowering Scientists Through Data!
With traditional drug testing methods often cumbersome and slow, Chen highlights the transformative potential of their AI-guided ChemPerturbDB. This open-access resource empowers scientists to navigate complex datasets with ease, thus accelerating the path to new, effective treatments.
Conclusion: Redefining Transplant Strategies!
This study not only showcases the importance of integrating AI and next-gen technologies into medical research but also emphasizes the need to consider sex differences in treatment outcomes. The findings from Weill Cornell Medicine could herald a new era for transplantation therapies, benefitting countless patients in their fight against diabetes.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)