Revolutionary Climate Model Exposes Hidden Consequences of 1°C Warming!
2025-07-18
Author: John Tan
Uneven Impact of Global Warming
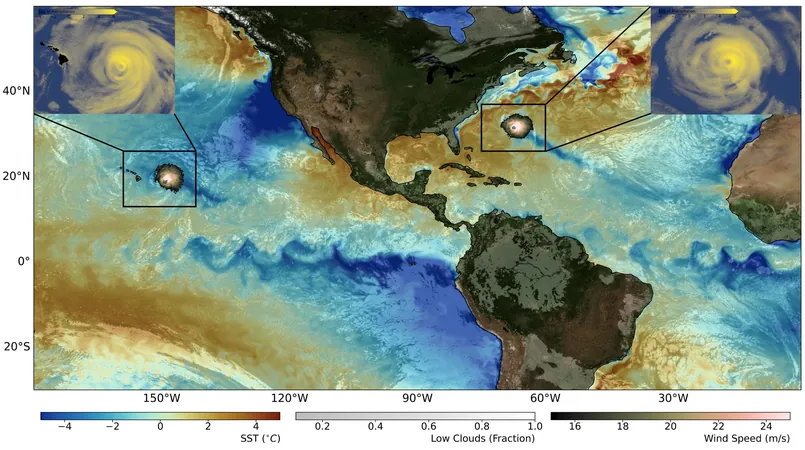
Global warming is not a uniform phenomenon; certain regions, like the Arctic and high mountain peaks, are experiencing heat waves far exceeding the global average, while tropical ocean areas are surprisingly cooler. To effectively address climate change, we need hyper-localized climate data, typically at a resolution much finer than the usual 100-200 km provided by the IPCC.
Breakthrough in Climate Modeling
A groundbreaking research team from the IBS Center for Climate Physics in South Korea, along with the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany, has developed a high-resolution climate model that delivers extraordinary insights into our planet’s future climate dynamics. Their findings, published in the journal Earth System Dynamics, promise to revolutionize how we understand and respond to climate change.
Cutting-Edge Technology at Work
Using the state-of-the-art AWI-CM3 Earth system model and the computing power of South Korea's supercomputers, the researchers have simulated climate changes at unprecedented detail—9 km in the atmosphere and 4-25 km in the oceans. This precise granularity enables a more realistic projection of future climate scenarios, facilitating better planning and adaptation strategies.
Mapping Future Climate Scenarios
One of the standout creations from this research is a comprehensive series of global maps predicting climate changes such as temperature changes, rainfall patterns, and wind dynamics for a projected global warming of 1°C. "In regions like Siberia and the Canadian Arctic, we anticipate temperature increases of about 2°C, and up to 5°C in the Arctic Ocean itself," shares lead author Moon Ja-Yeon. Mountain ranges like the Himalayas are expected to heat up a staggering 45%-60% more than the global average.
Interactive Data Platform Launched!
To make this vital information accessible, the researchers have rolled out an interactive data platform. Users can explore and visualize future climate changes both regionally and globally, downloadable straight into Google Earth. This platform will equip stakeholders with crucial data regarding forthcoming climate variables that will impact everything from wind energy deployment to solar farm placements.
Understanding Climate Variability
Moreover, the study also examines how significant climate variability modes—such as the Madden Julian Oscillation and El Niño-Southern Oscillation—will respond to greenhouse gas emissions. The projections indicate an increase in the strength and frequency of extreme rainfall events in vulnerable areas, with potential devastating impacts such as flooding, erosion, and landslides.
A Call for Action
Current global climate models often fail to capture the precarious situations of small island nations, which face rising sea levels. This innovative new model presents a golden opportunity to fill those gaps, giving planners and decision-makers the insights they need to tackle future climate challenges effectively. As Prof. Axel Timmermann emphasized, this information will be invaluable for assessing climate risks and informing adaptation strategies.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)