Alarm Bells Ring for India: Surge in Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales Shakes Healthcare System
2025-08-26
Author: Li
Understanding the Threat: What are Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales?
In a striking revelation, a recent study spotlighted the rising menace of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) in a tertiary care hospital in Bihar, India. Conducted over two years, from July 2021 to July 2023, this exhaustive survey aimed to understand the prevalence, phenotypic characteristics, and antibiotic resistance profiles of these dangerous pathogens.
The Study: Scope and Methodology
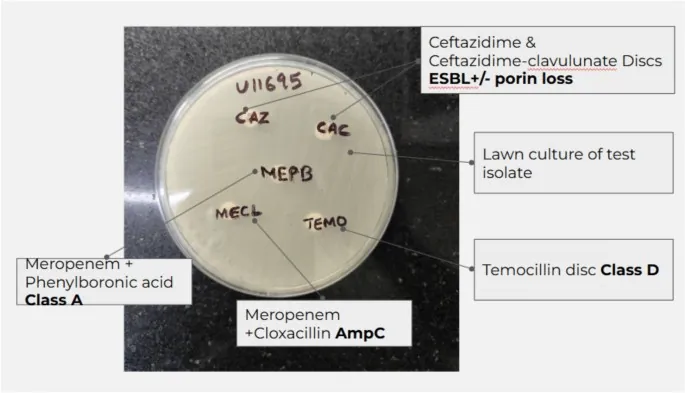
The cross-sectional study, approved by the AIIMS Patna Institutional Ethics Committee, focused on both outpatient and inpatient populations. Utilizing the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion technique, researchers examined 163 CRE isolates for resistance patterns and antibiotic efficacy to paint a comprehensive picture of this troubling trend.
Shocking Statistics: CRE Prevalence Uncovered!
Among the 3421 Enterobacterales samples tested, a staggering 32.97% were found to be carbapenem-resistant. This includes a concerning 47.74% resistance rate among inpatient samples, particularly prevalent in respiratory specimens. The leading offenders included Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli, responsible for a significant share of these inflections.
Alarming Antibiotic Resistance: The Data Speaks for Itself
This study reveals a chilling resistance profile among CRE isolates: 100% resistance to third-generation cephalosporins and nearly all tested isolates resistant to Beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations. As if that wasn’t enough, most CRE isolates showed resistance to fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides, severely limiting treatment options and raising alarms in the medical community.
Going Beyond the Numbers: The Phenotypic Breakdown
Further analysis unearthed that an astounding 95.77% of isolates tested positive for carbapenemase enzymes. Among these, the Class B metallo-beta-lactamases were the most prevalent, indicating a formidable challenge for treatment and infection control.
What Does This Mean for Public Health?
The staggering prevalence of CRE is not just a number—it's a dire warning. Factors like increasing use of antibiotics in healthcare, and even agriculture, coupled with deficient infection control protocols, have fostered an environment where these superbugs can thrive. The implications for public health are grave, necessitating an urgent need for enhanced surveillance and robust infection control measures.
Call to Action: What Can Be Done?
This study urges urgent interventions—including strict adherence to antibiotic stewardship, rigorous infection control, and innovative treatment strategies. As global health systems grapple with the ramifications of antibiotic resistance, India’s experience offers critical lessons in combating this escalating threat. The time for decisive action is now; the health of millions hangs in the balance.
Conclusion: A Growing Crisis on Our Doorstep
As the war against antibiotic resistance presses on, the findings from Bihar serve as a clarion call for healthcare systems worldwide. Strengthening our resolve to tackle CRE through coordinated efforts in research, policy, and practice is not just recommended but essential. The crisis of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales is not just an issue for India, but a challenge that affects global healthcare—and it is time we act.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)