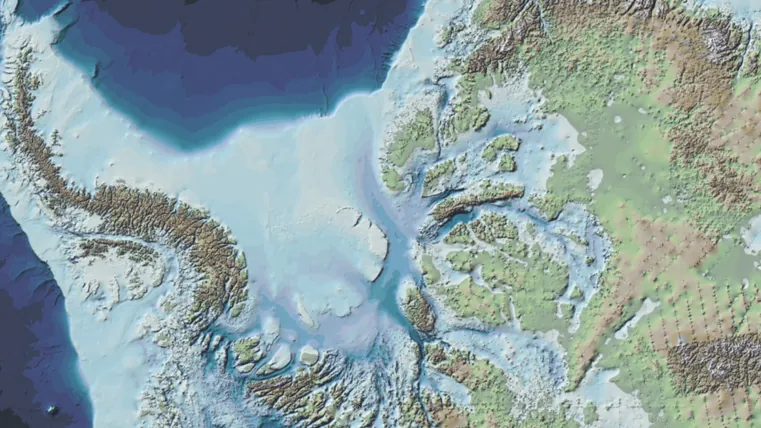
Shocking New Map Reveals Antarctica's Hidden Landscape – Are We in Greater Danger Than We Think?
2025-03-19
Author: Ting
Introduction
Scientists have released a groundbreaking new map detailing the hidden landscape beneath Antarctica's thick ice cover, offering unprecedented insights into the continent that could change our understanding of climate change impacts.
Unveiling Bedmap3
This high-resolution map, known as Bedmap3, not only uncovers the intricate topography of Antarctica below its extensive frozen layers but also provides crucial information for predicting how the continent might respond to the accelerating warming of our planet. According to Hamish Pritchard, a glaciologist at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) and the lead author of the study, the map acts as an essential guide for understanding where and how the ice will flow as temperatures rise. “Imagine pouring syrup over a rock cake – all the lumps and bumps determine where the syrup goes and how fast. The same principles apply to the melting ice sheet in Antarctica,” he explained.
A Historical Perspective
Bedmap3 is built upon the foundation of two previous mapping initiatives, incorporating vast amounts of information gathered over more than six decades. By leveraging 52 million additional data points sourced from technology ranging from satellites to radar, the new map significantly refines our knowledge of Antarctica's subglacial features. Now colored to illustrate the height of the bedrock above sea level, it captures the continent’s dramatic mountain ranges and deep valleys in astonishing detail.
Unexpected Discoveries
One of the most surprising findings from the research is the discovery of the thickest ice in Antarctica, located in an unnamed canyon in Wilkes Land, rather than the previously believed Astrolabe Basin. With an ice thickness of nearly 3 miles (4.8 kilometers), Wilkes Land's ice surpasses Astrolabe Basin’s thickness of about 2.9 miles (4.7 kilometers), highlighting an urgent need to reassess previous assumptions regarding ice distribution in the region.
Understanding Ice Shelves
Moreover, Bedmap3 provides fresh perspectives on the shapes and sizes of the floating ice shelves at Antarctica's edges. Peter Fretwell, a co-author and findability specialist at BAS, emphasized the importance of this detail: “The Antarctic Ice Sheet is thicker and has a larger volume of grounded ice than we initially realized, much of which is situated below sea level. This positioning raises alarm bells since warmer seawater can easily infiltrate and undermine the ice.”
Implications of Findings
With this new information indicating a more vulnerable Antarctica than previously acknowledged, scientists warn that the risks associated with melting ice are greater than ever before. As global temperatures continue to rise, the implications for sea level rise and global climate patterns are alarming.
Conclusion
The release of Bedmap3 opens the door to new research opportunities, helping scientists understand the dynamics of ice flow and the potential consequences of climate change on one of the world’s most critical environments. It’s a wake-up call for policymakers and global leaders to take urgent action in combating climate change before it’s too late. Will this new insight into Antarctica spark a shift in environmental policy, or will we continue to ignore the signs?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)