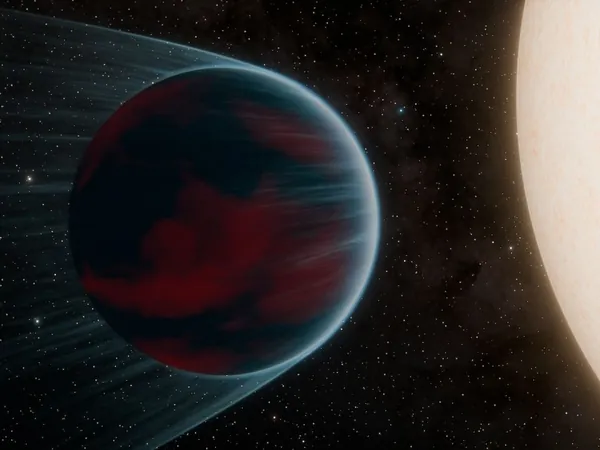

A Rare Discovery: Scientists Unveil a Shocking Planet in Neptune's Desert
2025-05-19
Author: Ken Lee
A Brand-New Cosmic Oddity Revealed
In an exciting development for astronomers, a new planet named TOI-3261 b has been discovered in the elusive region of space known as the "Neptune desert." This extraordinary find could challenge everything we think we know about planetary formation and evolution.
Meet TOI-3261 b: A Scorching Hot Neptune
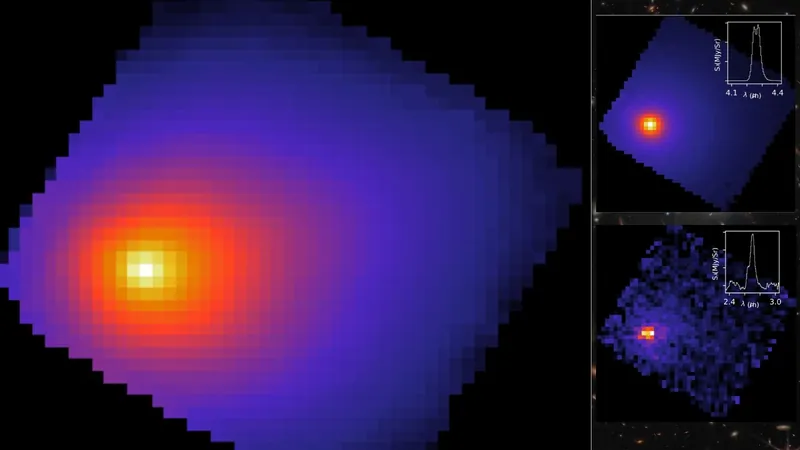
So what makes TOI-3261 b so special? It's categorized as a "hot Neptune" with a staggering yet swift orbit around its star—it completes a revolution in just 21 hours! To put that into perspective, Neptune takes a whopping 165 Earth years to orbit our Sun. The groundbreaking discovery was made by NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), which detects exoplanets by measuring tiny declines in starlight.
Unraveling the Mystery of the Neptune Desert
This newly discovered planet resides in a cosmic area mysteriously deficient in Neptune-sized planets with short orbits, called the "Neptune desert." While larger gas giants like hot Jupiters and smaller rocky planets known as super-Earths inhabit this zone, Neptunes are remarkably rare.
An Unexpectedly Dense World Awaiting Investigation
Following TESS's find, astronomers across Chile, South Africa, and Australia verified the planet's existence, revealing one astonishing detail: TOI-3261 b has an unusually high density for a planet of its kind. Initial research published in The Astronomical Journal suggests that instead of being filled with light gases like hydrogen and helium, this peculiar planet is likely rich in heavier elements, hinting it may have lost much of its original atmosphere.
A Planet's Story of Transformation and Loss
Interestingly, TOI-3261 b may not always have looked like this. Researchers believe it started as a gas giant, much larger than it appears today, before being stripped down over billions of years. Two key processes are thought to be responsible for this transformation: intense radiation from its star leads to photo-evaporation, while gravitational stripping occurs when tidal forces tug away a planet’s outer layers.
It's theorized that TOI-3261 b was originally formed around 6.5 billion years ago, probably much farther from its star than its current tight orbit suggests. Its disruptive migration could explain both its odd placement and compact structure. This scenario might also extend to three other known hot Neptunes in this remarkable region of space.
Significance: Why TOI-3261 b Matters
The discovery of planets like TOI-3261 b isn’t merely about curiosity; it’s vital for piecing together the broader narrative of planetary evolution. Every unique world invites scientists to refine their models and deepen their understanding of the cosmos. With powerful tools like TESS and the upcoming observations from the James Webb Space Telescope, the quest to uncover the mysteries of our universe is more promising than ever.
In a realm where surprising revelations often lead to groundbreaking insights, TOI-3261 b serves as a dazzling reminder that the cosmos is filled with wonders waiting to be explored.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)