James Webb Space Telescope Unveils Shocking Secrets of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS!
2025-08-26
Author: Yan
A Historic First Look at an Interstellar Voyager
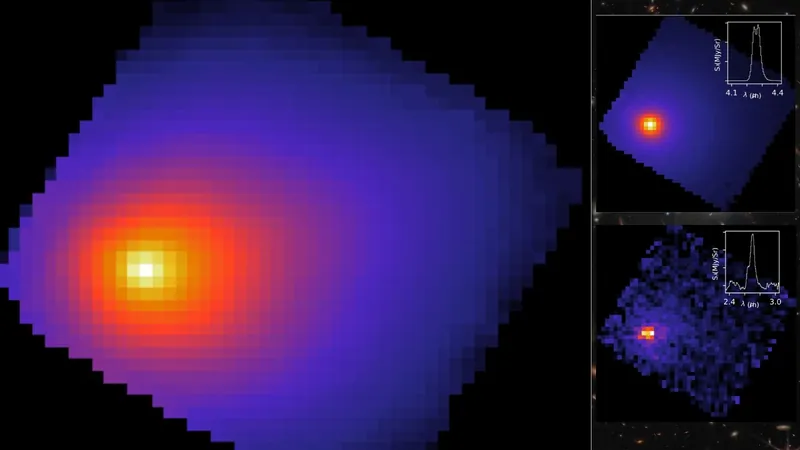
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has achieved a groundbreaking milestone by capturing its inaugural images of the interstellar traveler 3I/ATLAS on August 6, 2025. This comet, which was detected by the ATLAS survey telescope on July 1, is only the third known object from another star to drift through our solar system.
Unraveling Mysteries of Cosmic Origins
While the Hubble Space Telescope and the SPHEREx Observatory have previously glimpsed 3I/ATLAS, JWST's detailed investigation promises to uncover vital information about this celestial body, including its size, physical attributes, and most intriguingly, its chemical composition. By analyzing such comets, astronomers hope to gain insights into the primordial conditions of alien star systems, effectively drawing parallels with the environment of our own solar system 4.6 billion years ago.
Outgassing: The Comet’s Dramatic Transformation
As 3I/ATLAS approaches the sun, it undergoes a dramatic transformation. The intense heat causes frozen materials within it to turn into gas in a captivating process known as "outgassing," giving rise to its well-known tail and glowing coma. Recent findings from the JWST, utilizing its Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), have revealed an astonishing array of gases, including carbon dioxide, water, carbon monoxide, and even the pungent carbonyl sulfide.
An Unexpected Twist: High Carbon Dioxide Levels!
In a surprising twist, astronomers detected the highest ratio of carbon dioxide to water ever observed in a comet! This remarkable finding raises questions about the early environment in which 3I/ATLAS formed. It suggests that this interstellar comet might possess an icy core rich in carbon dioxide, possibly due to exposure to higher radiation levels compared to solar system comets.
A Clue to Its Extraordinary Origin!
The team speculates that the high levels of carbon dioxide could hint at the comet's formation near a "carbon dioxide ice line" within the swirling protoplanetary disk surrounding its parent star. This line is the threshold where temperatures cool enough for carbon dioxide to solidify.
More Mysteries Revealed!
Interestingly, the low amounts of water vapor in the comet's coma suggest that something may be blocking heat from reaching its icy core, affecting how water transforms from solid to gas compared to carbon dioxide.
The Ancient Voyager: A Spectacular 7 Billion Years in the Making!
Adding to the excitement, scientists believe that 3I/ATLAS may be up to 7 billion years old—making it the oldest comet ever observed! This age places it a staggering 3 billion years older than our solar system itself. Researchers deduced this incredible age from the steep trajectory of the comet, indicating its origins in the Milky Way's older "thick disk" of stars.
The Journey Continues!
With so many secrets still to be uncovered, the investigation of 3I/ATLAS is just beginning. The JWST is set to play a pivotal role in this cosmic quest, set to unveil more revelations before the comet returns to its interstellar home, leaving behind a treasure trove of knowledge!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)