Unveiling the Fascinating Similarities and Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells
2025-07-11
Author: Olivia
A Deep Dive into Cell Structure
Have you ever wondered what sets animal cells apart from plant cells? While both types share fundamental functions as the building blocks of life, their structures and capabilities tell an intriguing story!
Core Differences for a Better Understanding
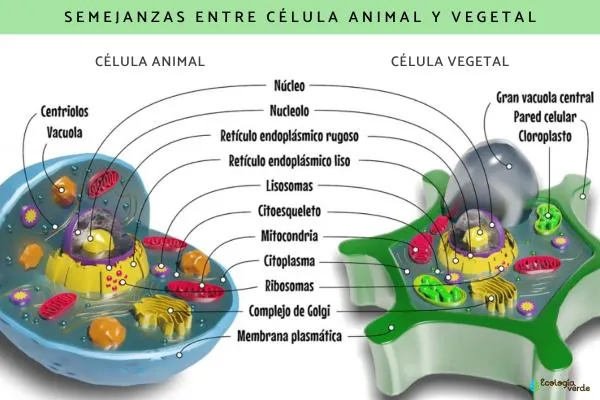
One of the most striking contrasts between these two cell types is the presence of the cell wall. Plant cells boast a sturdy cell wall in addition to their cell membrane, giving them a distinctive prismatic shape. Animal cells, on the other hand, rely solely on their flexible cell membrane.
Moreover, plants possess the remarkable ability to generate their own food through photosynthesis, a feat animal cells cannot achieve. This primary difference highlights the autonomy of plants in harnessing sunlight for energy.
The Essential Role of Cells in Life
Understanding the intricacies of animal and plant cells is essential for grasping how living organisms function. This knowledge can lead to breakthroughs in treating diseases and developing novel therapeutic techniques.
What Exactly is a Cell?
Cells are the fundamental units of life, capable of reproduction, growth, metabolism, and communication with their surroundings. They come in two forms: unicellular, like bacteria, and multicellular, encompassing both animals and plants. In multicellular organisms, cells work in harmony, signaling each other to coordinate responses to environmental cues.
Striking Similarities You Should Know
Despite their differences, animal and plant cells share significant similarities: 1. **Eukaryotic Structure**: Both are classified as eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a well-defined nucleus, organelles, and an organized genome. 2. **Plasma Membrane**: Each cell type is encased in a semipermeable plasma membrane, which regulates what enters and exits.
3. **Size**: They generally range between 10 and 100 micrometers, easily observable under a microscope.
Key Differences Unpacked
1. **Presence of Cell Wall**: While plant cells have a rigid cell wall composed mainly of cellulose, animal cells lack this structure, relying instead on their pliable plasma membrane. 2. **Unique Chloroplasts**: Chloroplasts—absent in animal cells—allow plants to perform photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy. 3. **Nutritional Methods**: Plant cells utilize autotrophic nutrition, making their own food, whereas animal cells are heterotrophic, requiring intake of organic substances. 4. **Vacuole Size**: In plant cells, large vacuoles dominate the cytoplasm, whereas animal cells contain smaller vacuoles. 5. **Centrioles**: Animal cells have centrioles for chromosome separation during cell division—this feature is absent in plant cells.
Shapes and Structures: A Visual Comparison
The shapes also diverge; plant cells often appear prismatic, while animal cells take on various forms. To aid in understanding, diagrams comparing the two cell types can be invaluable.
Summing It Up!
In essence, while animal and plant cells share foundational similarities as eukaryotic cells, their differences in structure, function, and nutrition are striking. For those eager to explore this topic further, engaging with visual resources like comparative charts can enhance your understanding.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore our biology category for more captivating articles on the wonders of life!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)