Unlocking the Secrets of RNA: Scientists Resurrect Ancient Protein to Transform RNA Research!
2024-12-02
Author: Olivia
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study, researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have resurrected an ancient version of a bacterial enzyme, paving the way for exciting advancements in RNA biology.
This innovative approach involves the engineering of an RNA methyltransferase that exhibits a significantly enhanced ability to chemically modify RNA, which could hold the key to understanding some of the most complex cellular processes.
Importance of RNA Modifications
The findings, published in the prestigious journal Nucleic Acids Research, highlight the critical role of RNA modifications in cellular health and disease.
These modifications influence key functions such as stability, translation efficiency, and the overall localization of RNA within cells.
Given these impacts, understanding RNA modifications is essential for unraveling the mysteries behind various diseases, including cancers and neurodegenerative disorders.
The Research Process
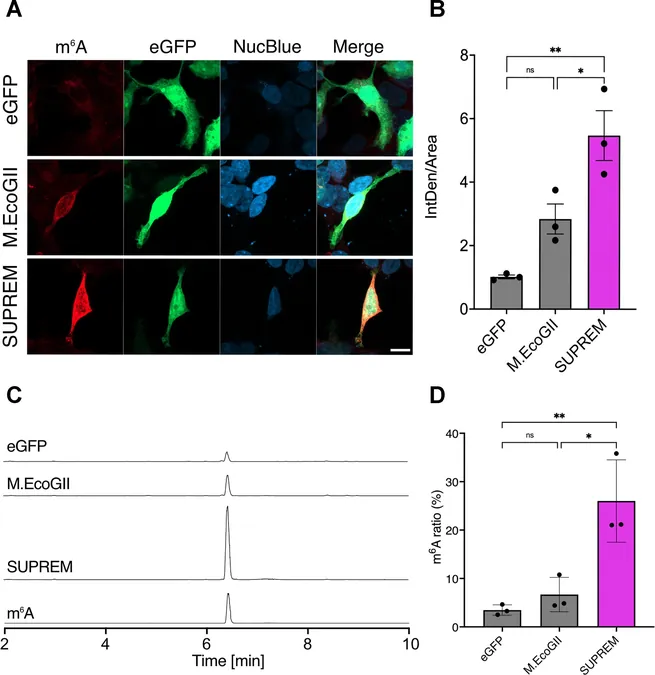
Yoshiki Ochiai, a Ph.D. student and the lead author of the study, meticulously worked to enhance the RNA methylation activity of a bacterial enzyme known as M.EcoGII, which previously displayed only a limited capability for RNA modification.
By utilizing bioinformatics to analyze the evolutionary background of this enzyme, the research team sought to identify its ancestral forms and determine whether they had been more effective as RNA or DNA methyltransferases.
Discovery of SUPREM
Through this analysis, the scientists reconstructed sequences from the enzyme's ancestors, leading to the discovery of a variant with exceptional RNA methyltransferase activity, aptly named SUPer RNA EcoGII Methyltransferase (SUPREM).
This newly engineered enzyme stands out not only for its remarkable selectivity towards RNA but also for its high methylation efficacy, demonstrating effectiveness even in mammalian cells.
Implications and Future Directions
The implications of this research are immense.
By harnessing SUPREM, scientists hope to develop advanced tools for probing intricate RNA modifications in a variety of diseases.
This could unlock new pathways for therapeutic interventions and provide insights that were previously beyond reach.
Conclusion
As the exploration of RNA biology continues, the resurrected SUPREM represents a monumental step forward, bridging the gap between ancient evolution and modern medicine.
Stay tuned as this research evolves, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of RNA and its critical functions in life!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)