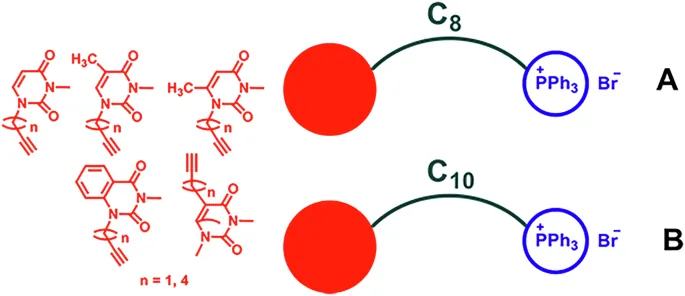
Unlocking the Power of Triphenylphosphonium Conjugates: A New Era in Antimicrobial Agents
2025-09-03
Author: Olivia
Revolutionizing Antimicrobial Strategies
In the relentless battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, scientists are turning their attention to innovative solutions. Among these, triphenylphosphonium (TPP) conjugates of various nucleic bases are emerging as a promising new class of antimicrobial agents.
Understanding Triphenylphosphonium Conjugates
Triphenylphosphonium compounds have long been studied for their potential in targeting mitochondria, particularly in the context of cancer therapy. Recent advancements have shown that these compounds can not only enhance the delivery of therapeutic agents to mitochondria but also exhibit strong antimicrobial properties.
Targeting Resistance: The Need for New Antimicrobials
Antibiotic resistance is a growing global issue, necessitating urgent solutions. Traditional antibiotics are becoming less effective, paving the way for a surge in research focusing on TPP and its derivatives. These compounds are showing promise in combating superbugs like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and various fungal pathogens.
Mechanisms of Action: How Do They Work?
The effectiveness of TPP conjugates lies in their unique ability to disrupt bacterial membranes. By compromising the structural integrity of microbial cells, they not only inhibit growth but can lead to cell death. This multifaceted approach opens new avenues for treating infections resistant to conventional antibiotics.
Recent Breakthroughs in Research
Recent studies have illuminated the potential of TPP-conjugated compounds in both antibacterial and antifungal applications. Innovations in synthesis and structure modification are enhancing their efficacy and selectivity, leading to compounds that target pathogens more effectively while sparing healthy cells.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Antimicrobial Therapy
As research progresses, the potential applications for TPP conjugates in clinical settings are becoming clearer. These compounds are not just adding to our arsenal against infection; they represent a shift towards more targeted and effective therapies that could transform the treatment of resistant infections.
In Conclusion: A New Hope in Antimicrobials
The exploration of triphenylphosphonium conjugates marks an exciting chapter in the quest for effective antimicrobial agents. With ongoing research, there is optimism that these unique compounds may soon play a critical role in combating antibiotic resistance and enhancing patient outcomes.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)