Unlocking the Power of Proteases: Revolutionary Bacterial Insights from the Red Sea
2025-09-01
Author: Jacques
The Multifaceted Role of Proteases
Proteases are nature's molecular scissors, expertly cleaving proteins at peptide bonds. This plays a critical role in cell growth, immune response, and metabolism, while also assisting in blood coagulation and facilitating protein transport across membranes. These versatile enzymes hold remarkable value across industries.
Industrial Marvels: Where Proteases Shine
In the detergent sector, alkaline proteases derived from Bacillus species efficiently tackle protein stains, promoting energy-efficient cold washing. The food industry exploits proteases for tenderizing meat, crafting cheese, enhancing soy products, and generating bioactive peptides to boost nutrition and texture. The pharmaceutical realm benefits as well, utilizing microbial proteases for treating cardiovascular, inflammatory, and digestive issues, while the leather industry embraces them for eco-friendly processing.
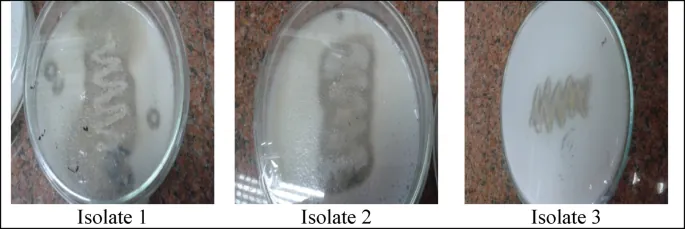
A Treasure from the Depths: Isolating Protease-Producing Bacillus
This study aimed to extract and improve enzyme production from new Bacillus strains discovered in the nutrient-rich waters off Ras Sedr, Red Sea. Using organic waste like defatted soybean cake, the researchers optimized conditions for enhanced protease yield, showcasing the potential of such biological technologies.
From Sea to Laboratory: Isolation and Analysis Procedures
Seawater samples collected at a depth of 15 meters served as the starting point for isolating protease-producing bacteria through nutrient agar. After meticulous screening using specialized agar mediums, the study pinpointed the standout strains, which were preserved for further analysis and characterization.
The Genetic Breakthrough: Identifying the Star Isolate
The most promising bacterial isolate was identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NRC-IB-11, showcasing remarkable protease production capabilities. Genetic sequencing confirmed its distinct position among Bacillus relatives, enhancing our understanding of this powerful enzyme producer.
Maximizing Production: The Role of Organic Waste
Utilizing low-cost organic waste materials like defatted soybean cake proved beneficial for enzyme production, with studies revealing that the cake amplified enzyme activity significantly compared to other substrates. This approach not only supports bioproduction but also aligns with sustainable practices by transforming waste into valuable resources.
Optimization of Enzyme Production: A Case Study with DSC
Through trials, researchers optimized several variables including substrate concentration, inoculum size, pH, and temperature. The team discovered that a substrate concentration of 10 g/100 mL yielded peak activity at 590 U/mL, emphasizing the balance needed between nutrient availability and enzyme synthesis.
Future Perspectives: Unleashing Industrial Applications
With Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NRC-IB-11 demonstrating an impressive tolerance for alkaline conditions and moderate temperatures, its proteases hold promise for diverse industrial applications, particularly in detergent and food processing. The findings open doors to cost-effective and scalable productions, providing a more sustainable approach to enzyme manufacturing in an industrial context.
Conclusion: A New Era for Bio-Enzyme Production
The journey from the depths of the Red Sea to innovative enzymatic applications highlights the potential of marine microorganisms in revolutionizing the enzyme industry. The study paves the way for further exploration and utilization of marine resources, reinforcing the significant role of biotechnology in sustainable practices.









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)