Unlocking Independence: How Nutritional Status Predicts Recovery After Hip Fracture Surgery in Seniors
2025-08-18
Author: Charlotte
Background: A Growing Concern for the Elderly
Hip fractures pose a significant health risk for older adults, often stemming from falls due to weakened bones. Maintaining the ability to perform basic activities of daily living (BADL) is crucial for long-term health outcomes. Recent research has delved into the Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) as a potential predictor of functional independence following hip fracture surgery.
Study Insights: Tracking Recovery Over Two Years
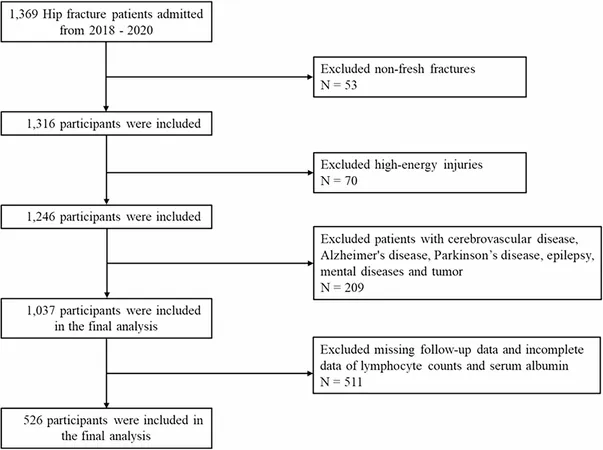
In a comprehensive analysis involving 526 older adults (average age 73) who underwent hip fracture surgery, researchers aimed to understand how preoperative PNI scores could indicate the risk of developing moderate-to-severe BADL dependence two years post-operation. Among the participants, 8.17% were found to have significant dependence upon follow-up.
Key Findings: Nutritional Status Matters
The study highlighted that individuals with higher preoperative PNI scores were less likely to face long-term dependence, with an odds ratio of 0.90 (meaning a 10% decrease in risk for each unit increase in PNI). This correlation remained strong even after conducting propensity score matching to control for other influencing factors.
The Stakes: The Soaring Costs of Hip Fractures
Hip fractures are not just a personal health concern; they represent a growing burden on healthcare systems, expected to escalate to $9.8 billion annually in the U.S. by 2040. With projections indicating that the number of affected individuals could rise from 4.5 million today to 21 million over the next forty years, understanding how to improve recovery outcomes is now more critical than ever.
The Role of Nutrition: A Call to Action
Recognizing the importance of nutritional health before surgery could be a game-changer for older patients. By identifying individuals at higher risk based on their PNI scores, healthcare providers can implement nutritional strategies—such as dietary changes or supplements—that may enhance recovery and independence.
Looking Ahead: Towards Better Recovery Protocols
This groundbreaking study urges the integration of nutritional assessments into preoperative care plans for older adults facing hip surgeries. As we continue to explore efficient recovery pathways, these findings could lead to improved quality of life for the elderly, allowing them to regain their independence post-surgery.
Conclusion: A New Perspective on Surgical Recovery
In conclusion, the PNI emerges as a vital predictor of recovery potential following hip fractures in older adults. Future research should focus on validating these findings and developing targeted nutritional interventions that cater to improving postoperative outcomes in this vulnerable demographic.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)