Uncovering the Hidden Risk Factors of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Insights from Southwestern China
2025-08-27
Author: Michael
What Is OCD, and Why Is It on the Rise?
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not just a quirky habit but a serious mental health condition affecting 2.0–3.0% of the global population. This places it as the fourth most prevalent mental disorder, rivaling conditions like asthma and diabetes. As figures climb, traditional treatments seem increasingly ineffective, highlighting the urgent need for research into risk factors and prevention strategies.
Genetic vs. Environmental Influences: The Debate Continues
Research suggests that OCD stems from a blend of genetic predispositions and environmental experiences. Families and twin studies reveal a hereditary element, where first-degree relatives of individuals with OCD are at a higher risk. However, the relationship between specific genes and OCD remains a topic of debate, indicating that we still need thorough investigations.
The Shocking Link Between Gut Health and OCD
Recent findings show that nearly 40% of OCD patients suffer from gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Poor gut health, influenced by diet and lifestyle, could exacerbate mental health issues. As nutritional habits shift, the interplay between gut microbiota and mental wellness demands urgent research attention.
New Study Aims to Explore Risk Factors in the General Population
Conducted in southwestern China, our study aimed to illuminate the links between demographics, lifestyles, and dietary habits, and OCD risk, utilizing surveys from a general population of 1,572 participants. This innovative approach intends to create a foundation for targeted prevention programs to combat OCD.
Diving into Data: Who Are the Participants?
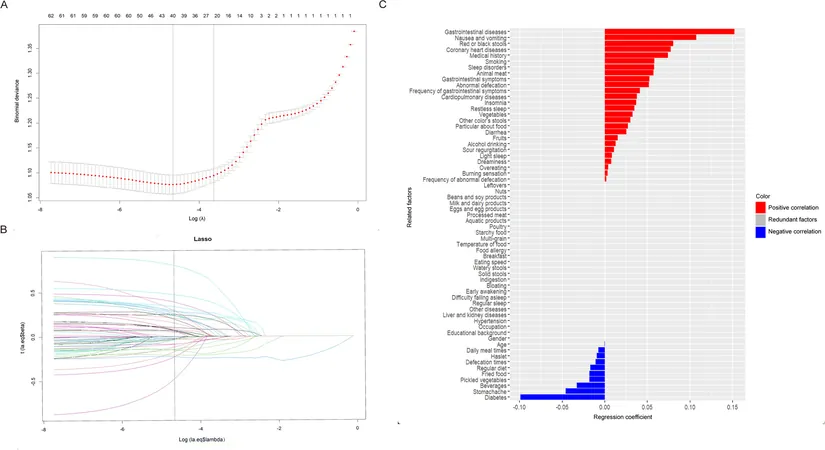
Among the survey participants, a majority were young adults, with more than half holding a bachelor's degree or higher. A concerning 30.4% were identified as high-risk for OCD, with significant findings on the demographic and lifestyle factors affecting this risk.
Trends and Insights from the Research
Notably, men exhibited higher rates of high-risk OCD than women—a finding that contrasts with many past studies. Furthermore, lifestyle factors such as smoking, sleep quality, and even dietary diversity (with picky eaters showing higher risk) emerged as influential contributors.
The Impact of Sleep and Gastrointestinal Issues
Poor sleep quality and GI symptoms were alarming red flags. Participants dealing with these issues had significantly higher OCD risk, suggesting that what’s happening inside our bodies—like how our gut behaves—can profoundly influence our mental state.
The Importance of Healthy Habits
Interestingly, those who abstained from regular beverage consumption were found to have lower OCD risks. This raises questions about how dietary choices might stabilize emotional health and protect against mood disorders.
Breaking Ground on Future Research
This study, emphasizing a general population approach in an under-researched area, sets the stage for future investigations. However, we must tread carefully; correlations do not imply causation. Further long-term studies are needed to firmly establish the intricate web of factors affecting OCD.
A Call to Understand and Act
Understanding the underlying causes of OCD is crucial for effective intervention and public health strategies. If you or someone you know struggles with OCD, seeking help is paramount. We must elevate awareness and encourage more individuals to share their experiences, fostering a healthier dialogue around mental health.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)