Unlocking Ethical Safety: A Game-Changer for Healthcare Professionals Across Europe
2025-09-09
Author: William
Understanding Ethical Safety in Healthcare
Ethical safety is paramount in healthcare, allowing professionals to uphold their values while providing patient care. This concept hinges on four core elements: general ethical safety, ethical autonomy, ethical respect, and ethical confidence. These pillars encompass three critical dimensions: the patient, healthcare professionals, and their working environment.
The Impact of Ethical Competence on Patient Care
Studies have shown that a robust ethical foundation among healthcare professionals significantly enhances both patient outcomes and job satisfaction. When staff possess ethical competence, they demonstrate moral courage, allowing them to navigate complex dilemmas and safeguard patient rights. However, the disconnect between knowing the right decision and acting upon it can lead to moral distress, creating ethically unsafe environments that compromise patient care.
Introducing the Ethical Safety Questionnaire (ESQ)
To tackle this issue, the Ethical Safety Questionnaire (ESQ), devised by Tarja Poikkeus, measures ethical safety in healthcare settings. This tool focuses on four key components and evaluates the ethical climate among nurses and physiotherapists, who are often at the forefront of care. Despite its promise, the ESQ's psychometric properties were previously untested, necessitating a thorough evaluation.
Objective: Validating ESQ Across Europe
The primary aim of this study was to validate the psychometric properties of the ESQ in acute healthcare environments across Finland, Sweden, Latvia, and Malta. This descriptive cross-sectional study sampled 275 healthcare professionals to ensure a diverse representation.
Rigorous Research Design and Methodology
Participating healthcare professionals, including nurses and physiotherapists, were invited based on their permanent employment status, with over 200 completing the ESQ. The survey’s data collection spanned three months, utilizing Webropol 3.0 for anonymity and convenience.
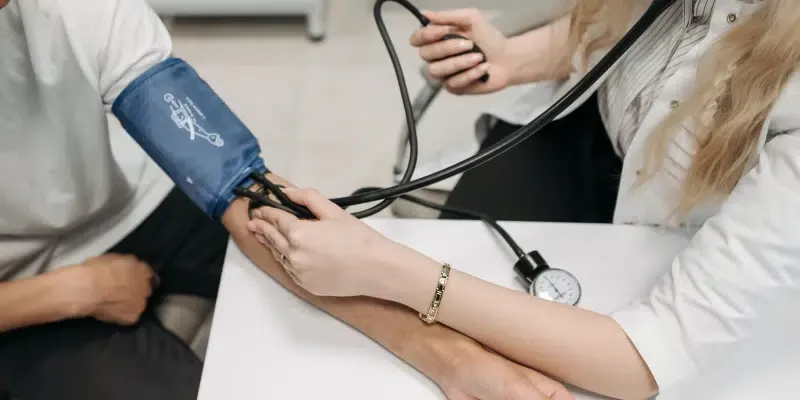
Results: A Sound Measure of Ethical Safety
The results confirmed the ESQ’s reliability. Internal consistency was shown through high Cronbach’s alpha coefficients, indicating that the three subscales—ethical autonomy, ethical respect, and ethical confidence—effectively measure the underlying concept of ethical safety. Furthermore, exploratory factor analysis revealed that the tool accurately captures the multifaceted nature of ethical safety.
Implications for Future Practice
The study elucidates the intricate relationships between ethical decision-making and professional autonomy within healthcare. By fostering environments where healthcare professionals feel respected and valued, organizations can significantly enhance ethical safety. Emphasizing trust and collaboration across disciplines can mitigate moral distress and bolster job satisfaction.
Call for Continued Research and Action
With ethical competence emerging as a cornerstone of high-quality care, further research is essential to explore power dynamics and hierarchical structures impacting ethical practices. Implementing educational interventions can bolster the ethical competence of healthcare professionals, ultimately creating safer, more supportive healthcare environments.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Ethical Care in Healthcare
As validated by this study, the ESQ offers a reliable metric for assessing ethical safety among healthcare professionals. Through ongoing evaluations and targeted interventions, we can cultivate ethical workplaces that enhance the quality of care provided to patients while supporting the wellbeing of healthcare providers.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)