Unlocking Drug Discovery: Ubiquitin’s Game-Changing Role in Targeting Disease Proteins
2025-09-17
Author: Charlotte
Ubiquitin: The Tiny Powerhouse of Cellular Control
Ubiquitin may be small, but its impact on cellular processes is huge! This tiny protein not only manages the lifespan and distribution of proteins within cells but intricately determines their shape, function, and interactions with other cellular components. Central to this process are ubiquitin ligases—vital players that skillfully identify relevant proteins amid thousands and deliver precise tagging instructions. When this tagging system falters, it can lead to severe cellular dysfunctions and diseases like cancer.
Revolutionizing Drug Design with Ubiquitin
Imagine being able to design drugs that modulate these ubiquitin ligases to mark disease-causing proteins for destruction. While this promising principle has been explored, it is applicable only to a handful of the over 600 ubiquitin ligases in the human body.
Meet HUWE1: A Hidden Gem in Therapeutic Strategies
Among these ligases, HUWE1 stands out as a captivating yet underutilized target, especially due to its significant roles in tumors and neurodevelopmental disorders. Despite the use of drug-like compounds to inhibit HUWE1 in research, their precise working mechanism remained shrouded in mystery—until now.
A Breakthrough Discovery by a Dedicated Research Team
A groundbreaking study led by Sonja Lorenz at the MPI for Multidisciplinary Sciences has finally unveiled how these compounds interact with HUWE1. By employing an innovative mix of protein biochemistry, cell biology, and click chemistry, the researchers pieced together the puzzle.
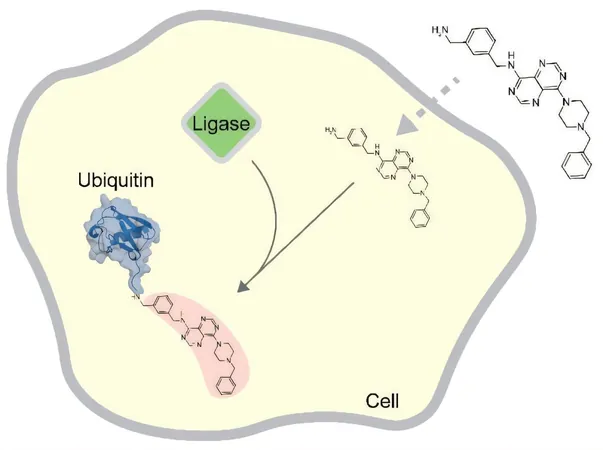
Uncovering the Unexpected: Competition Over Inhibition
The surprising revelation? These drug-like compounds do not inhibit HUWE1 as previously believed. Instead, they act as competitors! HUWE1 recognizes these compounds and tags them with ubiquitin. Pavel Pohl, one of the study’s leads, explains that when these compounds are over-supplied in a test environment compared to natural target proteins, they essentially consume the available ubiquitin.
Cellular Context Matters: Ubiquitin Tagging in Action
In a landmark finding, the research team demonstrated for the first time that these synthetic compounds are ubiquitinated within living cells. Yet, the dynamics are far more complex than in test tubes.
Barbara Orth, another lead author, notes that while HUWE1 catalyzes the ubiquitination of these compounds, it isn't the sole player in the game. This opens up new avenues, suggesting that other cellular ubiquitination enzymes may also tag these synthetic molecules—a revelation that transforms our understanding of cellular ubiquitination beyond just proteins and sugars to include synthetic compounds!
A New Era for Drug Discovery Awaits!
With this pioneering research, the door to innovative drug discovery strategies has swung wide open, potentially leading to effective therapies for various diseases. The future of targeted drug development is looking brighter than ever!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)