Unlocking Clean Water: Revolutionary 3D Nanotech Blankets Transform Pollution into Purity!
2025-03-24
Author: Liam
Introduction
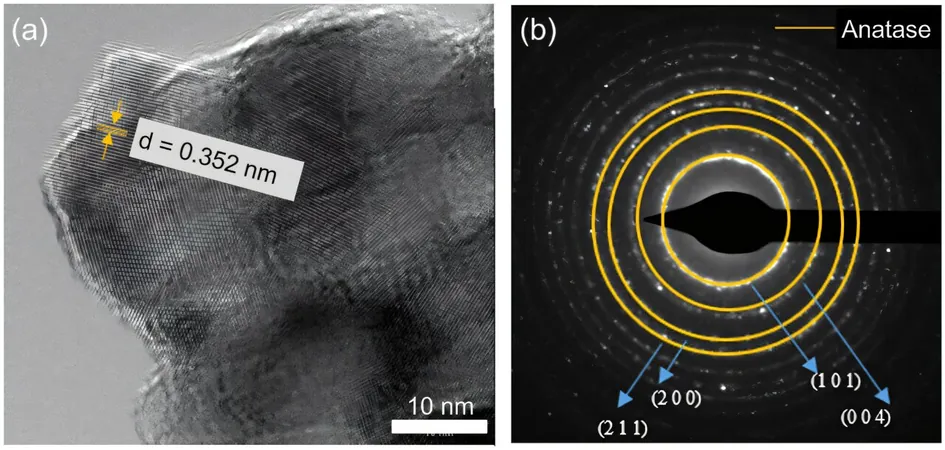
In a groundbreaking development, researchers at The Ohio State University have unveiled a cutting-edge material that uses the power of sunlight to purify water by eliminating harmful pollutants. These innovative thin fiber strips, known as nanomats, are made from titanium dioxide (TiO₂) through an advanced technique called electrospinning, which employs electrical force to generate tiny filaments from a liquid solution. TiO₂, a known player in solar cells and self-cleaning technologies, has now found a new life in water remediation.
The Advancement in Nanomats
Traditionally, solar fuel systems utilizing TiO₂ nanoparticles have faced significant challenges, primarily because they are limited to absorbing non-visible UV light. This constraint often results in low efficiency and the necessity for complex filtration solutions, hampering their widespread use. However, this new approach incorporated copper into the nanomats, enhancing their ability to absorb light and significantly improving the breakdown of hazardous substances present in both air and water.
Expert Insights
Pelagia-Iren Gouma, the lead author of the study, stated, 'There hasn’t been an easy way to create something like a blanket that you can lay on water and start creating energy. But we are the only ones who have made these structures, and the only ones to demonstrate that they actually work.' The innovation has been captured in a recent publication in the prestigious journal *Advanced Science*.
How It Works
When TiO₂ absorbs sunlight, it generates electrons that oxidize water and attack pollutants, eventually rendering them harmless. The inclusion of copper acts as a catalyst, amplifying this clean-up process. During their research, the team discovered that these nanomats surpass traditional solar cells in power generation capabilities under natural sunlight conditions.
Dual Purpose and Environmental Impact
Gouma added, 'These nanomats can serve dual purposes: as efficient power generators or as effective water remediation tools, boasting the highest efficiency rates recorded to date.' Remarkably lightweight and effortlessly deployable, these fiber mats can float on any water surface and are not only reusable through multiple cleaning cycles, but they also pose no environmental hazards. 'It’s a safe material, it won’t hurt anything, and it’s as clean as it can be,' Gouma emphasized, highlighting their sustainability.
Commercial Viability and Future Prospects
While this revolutionary technology shows immense promise, its commercial viability depends on timely industrial adoption. 'We possess the capacity to produce these nanomats in large volumes and apply them across various sectors,' Gouma stated. 'The only limit is harnessing these abundant resources.'
Broader Applications
Experts believe that the potential applications for nanomats extend far beyond pollution cleanup. They could play a pivotal role in long-term sustainability projects, including solar-driven hydrogen production and extensive environmental remediation efforts.
Conclusion
As the team looks forward, they are committed to optimizing this material further, excited about the prospects it brings to the field of nanotechnology. 'This material is entirely new in terms of a novel form of nanotechnology,' Gouma concluded. 'It’s impressive and something that we are genuinely thrilled about.'
Call to Action
Stay tuned as these innovative nanotechnology blankets pave the way to a cleaner, safer future for drinking water worldwide – a game changer in the fight against water pollution!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)